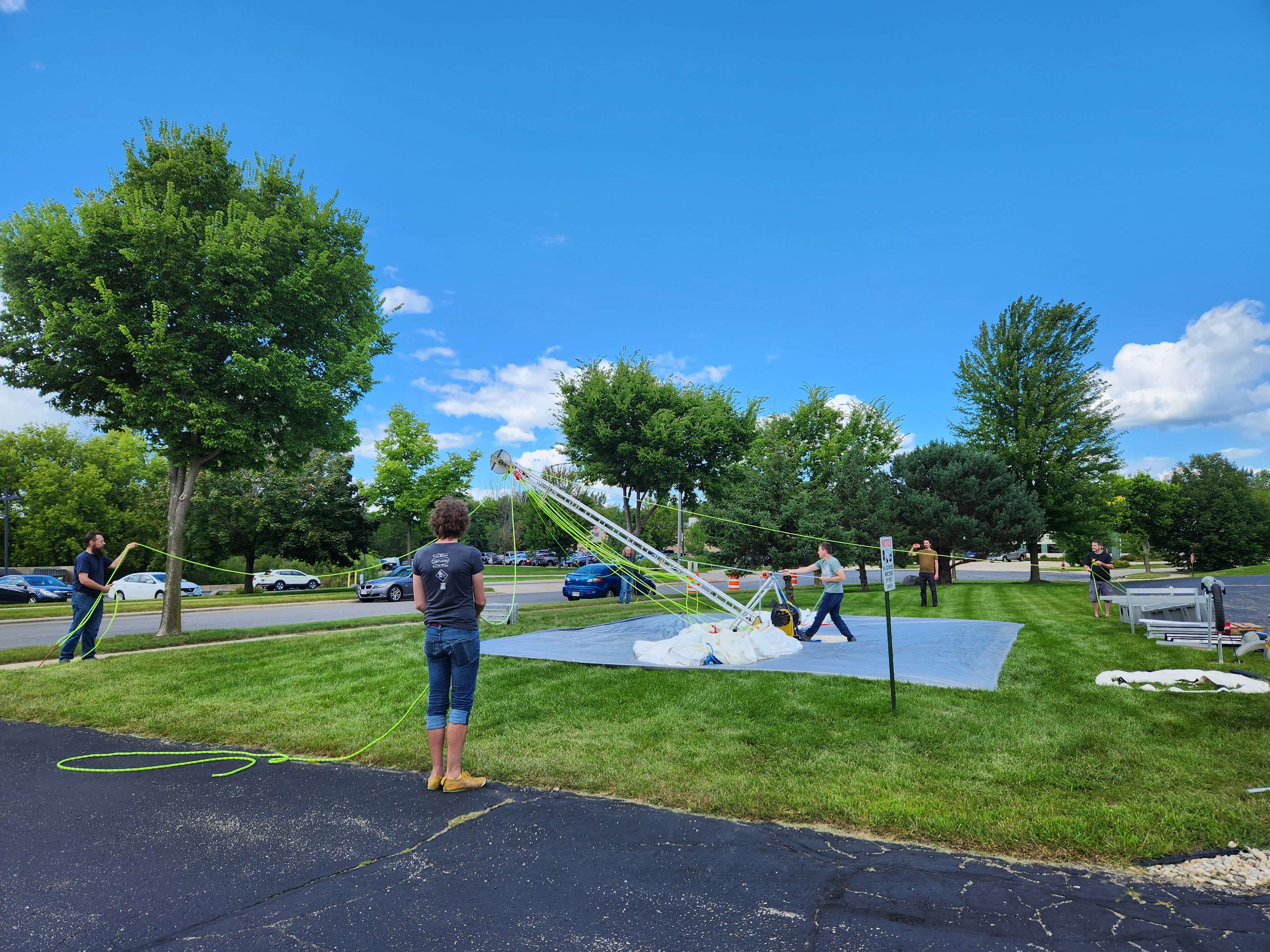
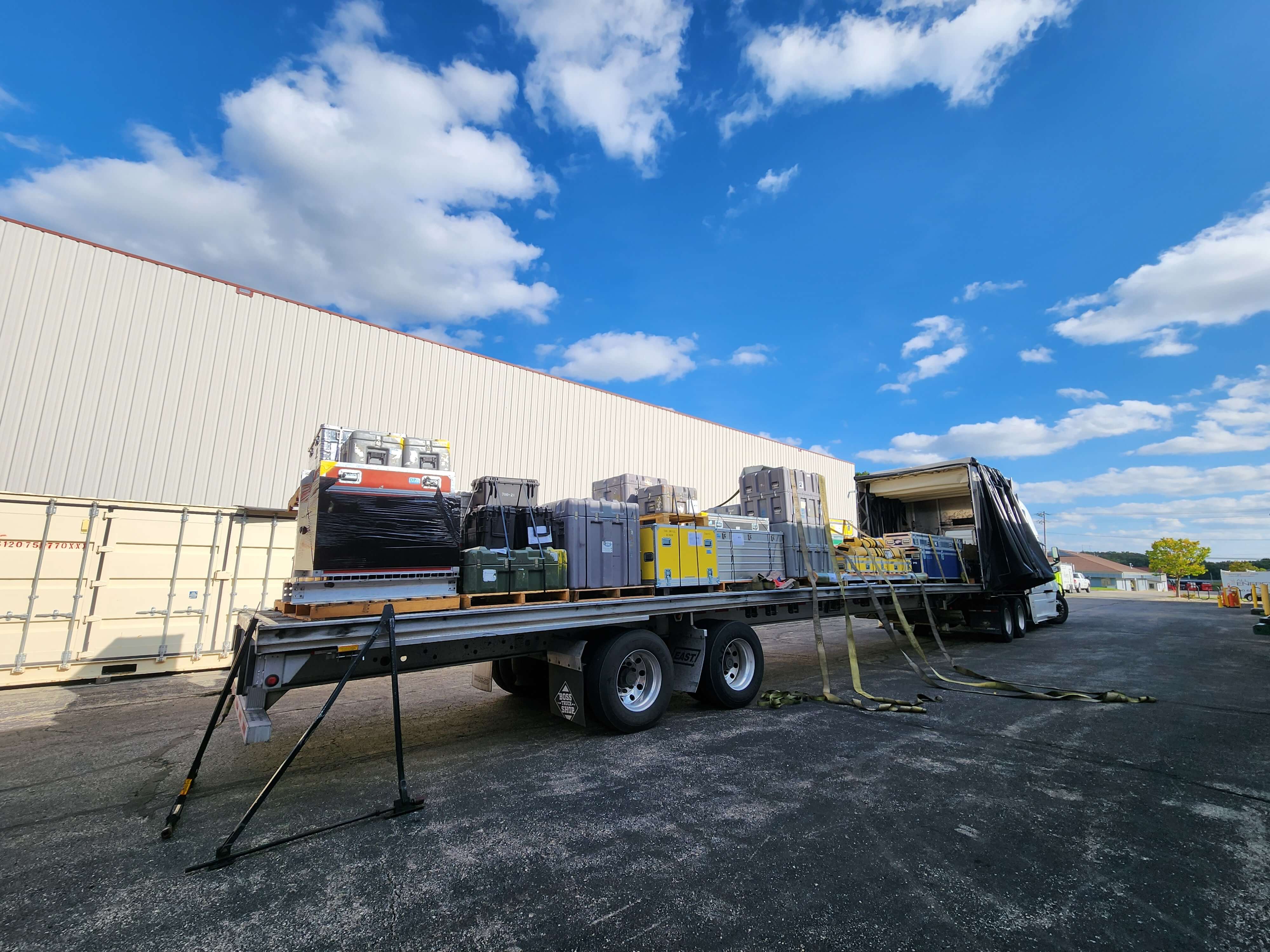
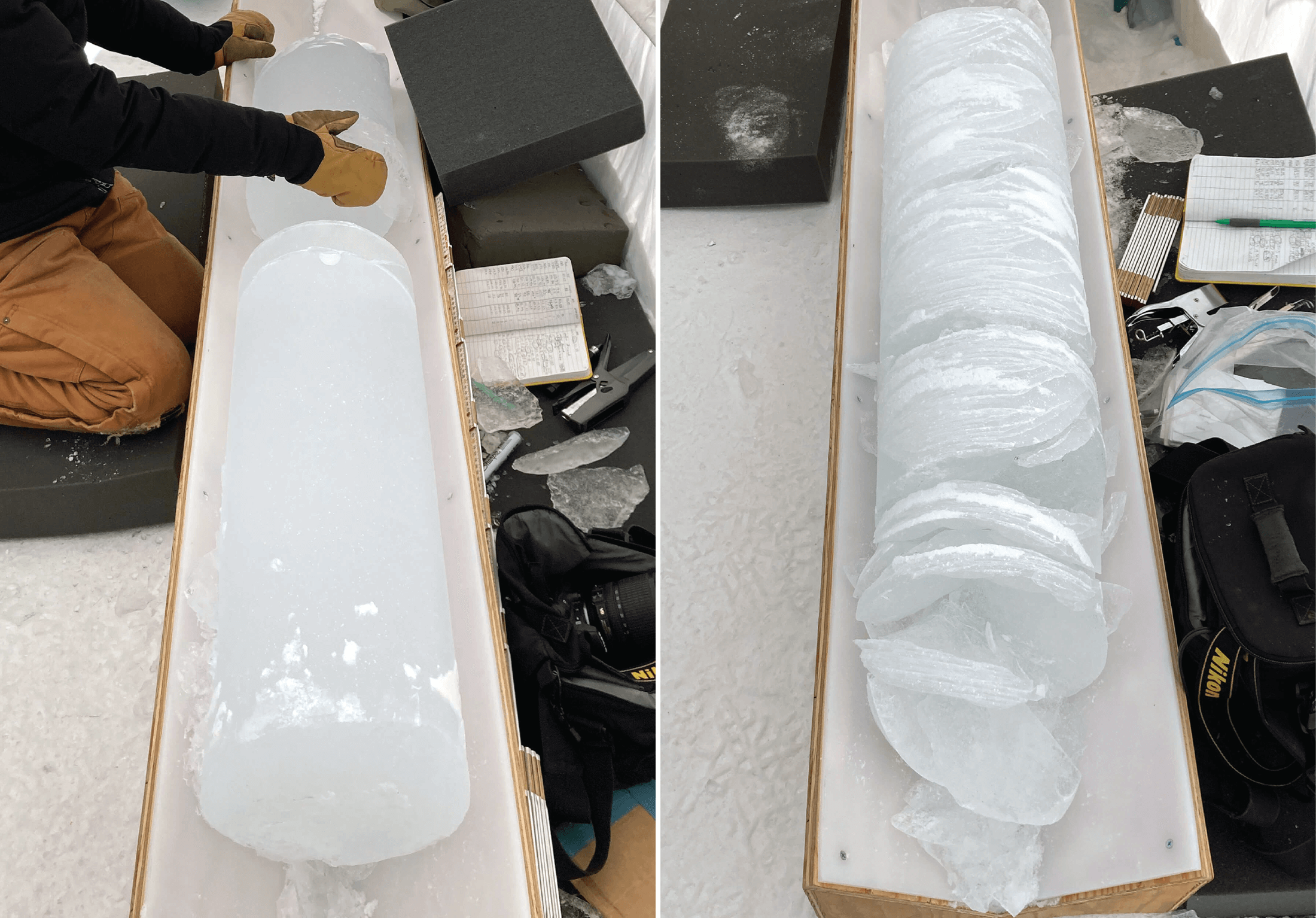
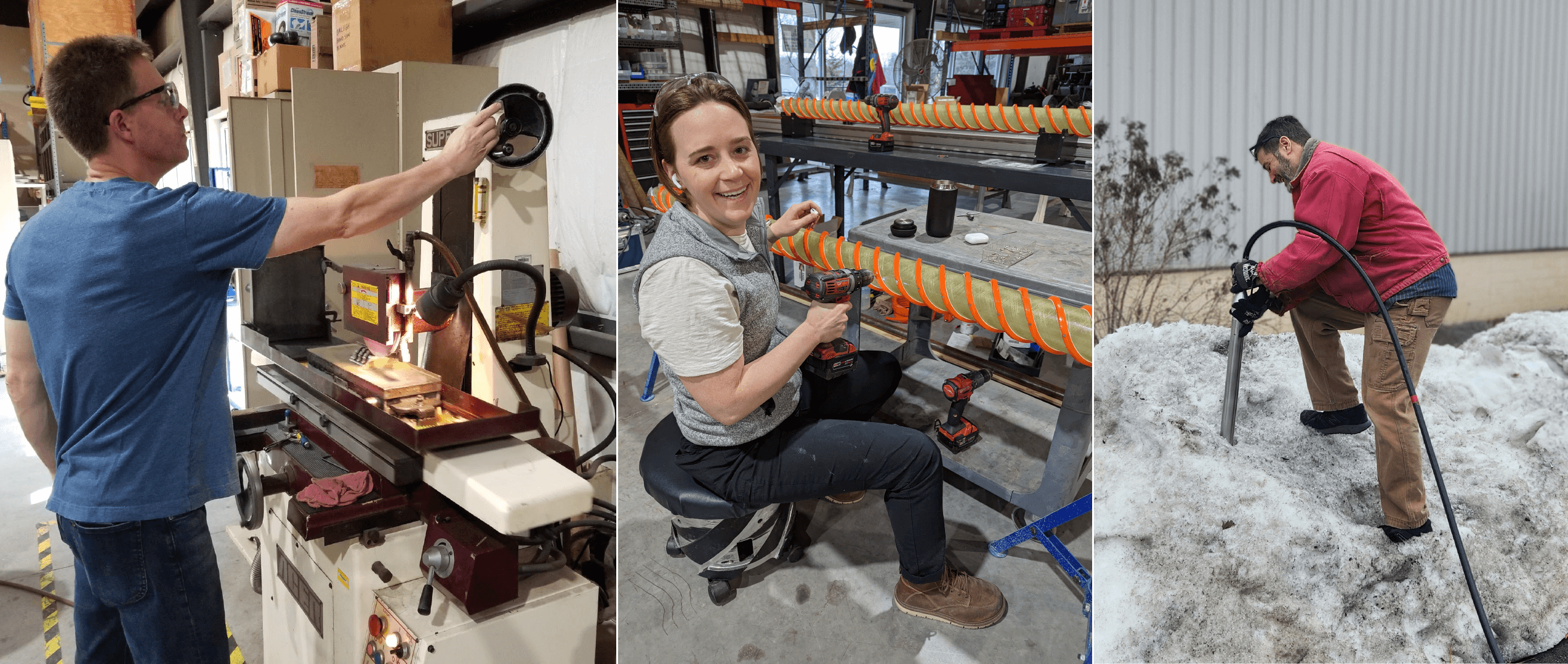
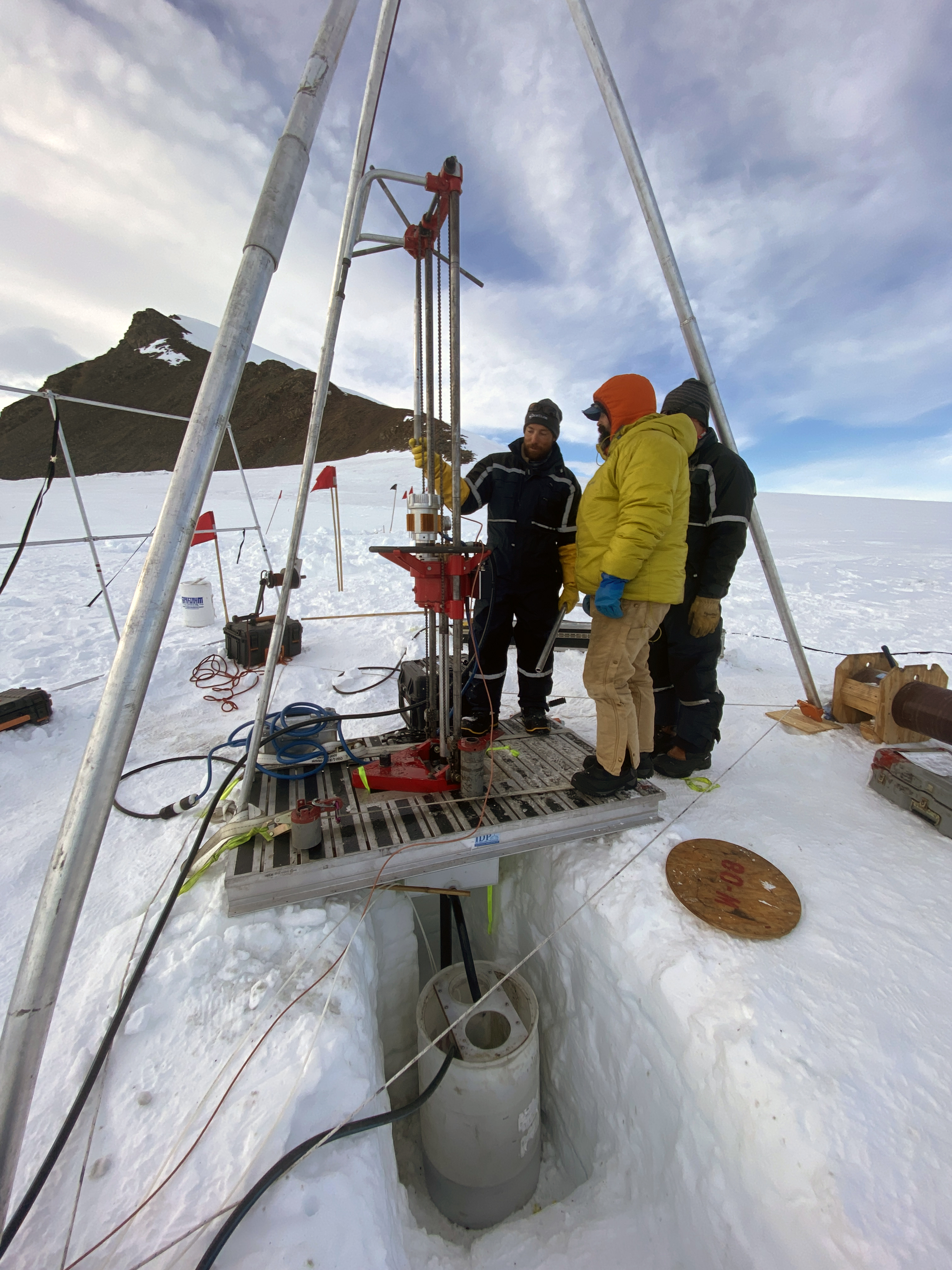
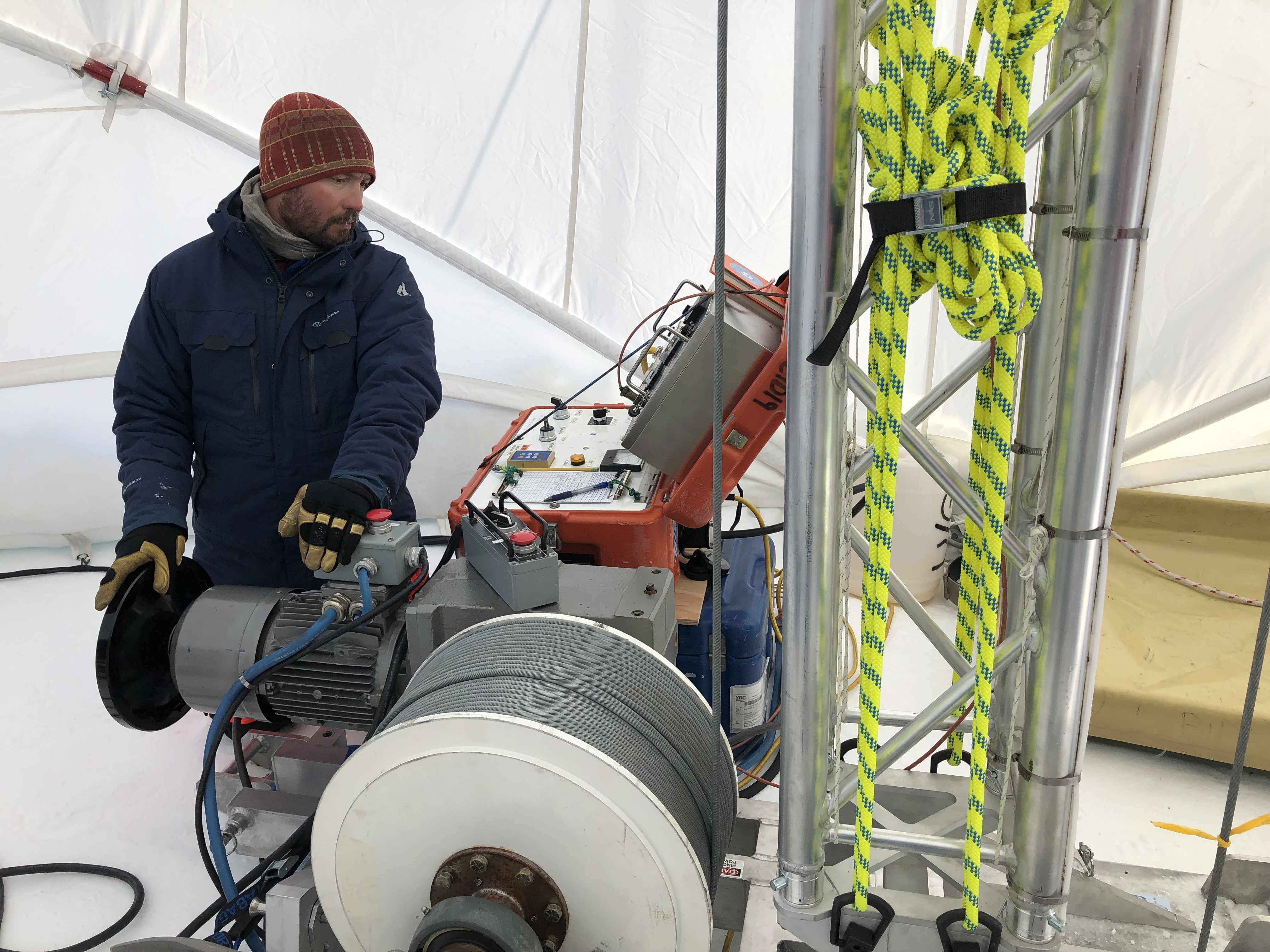
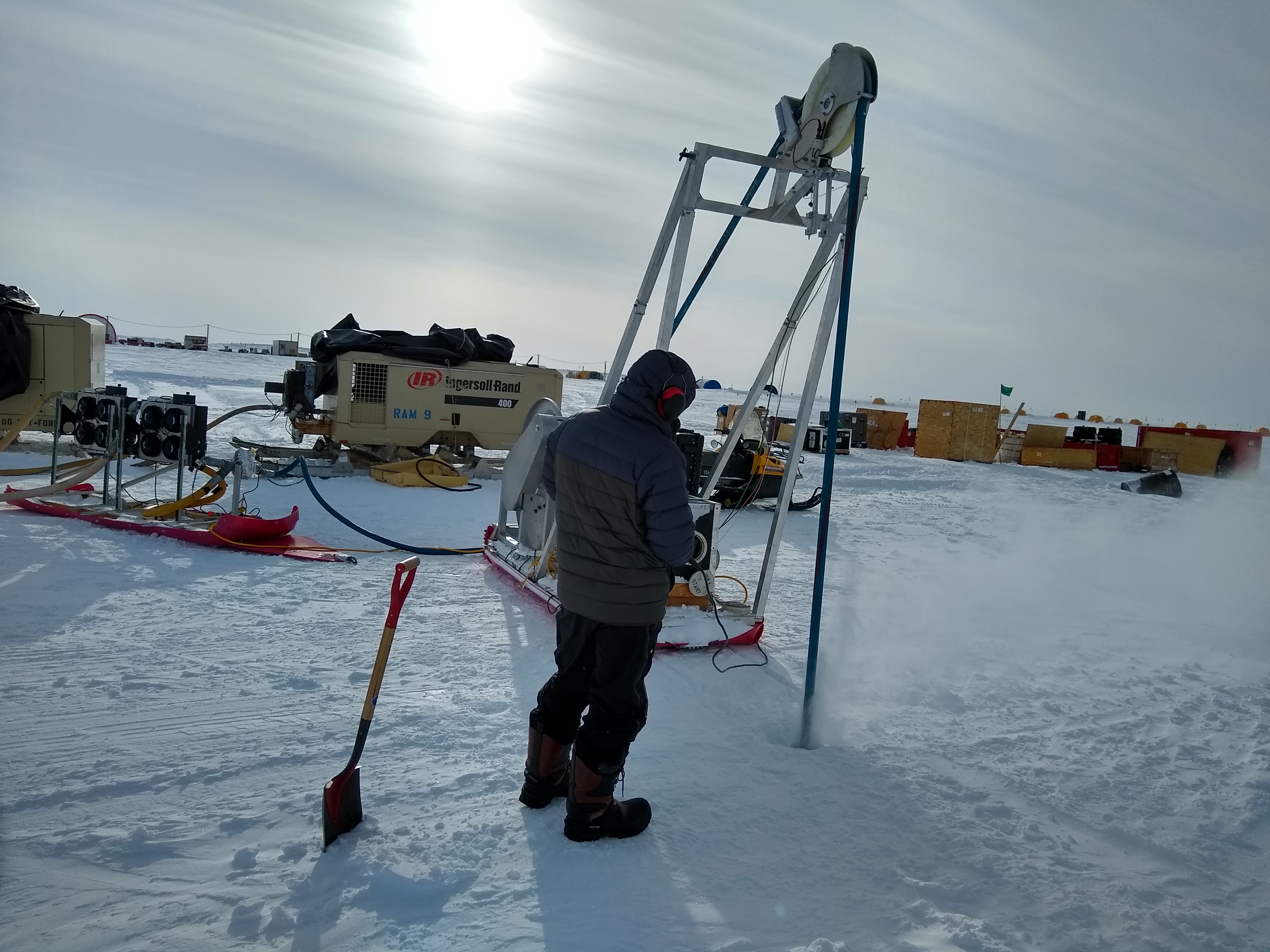
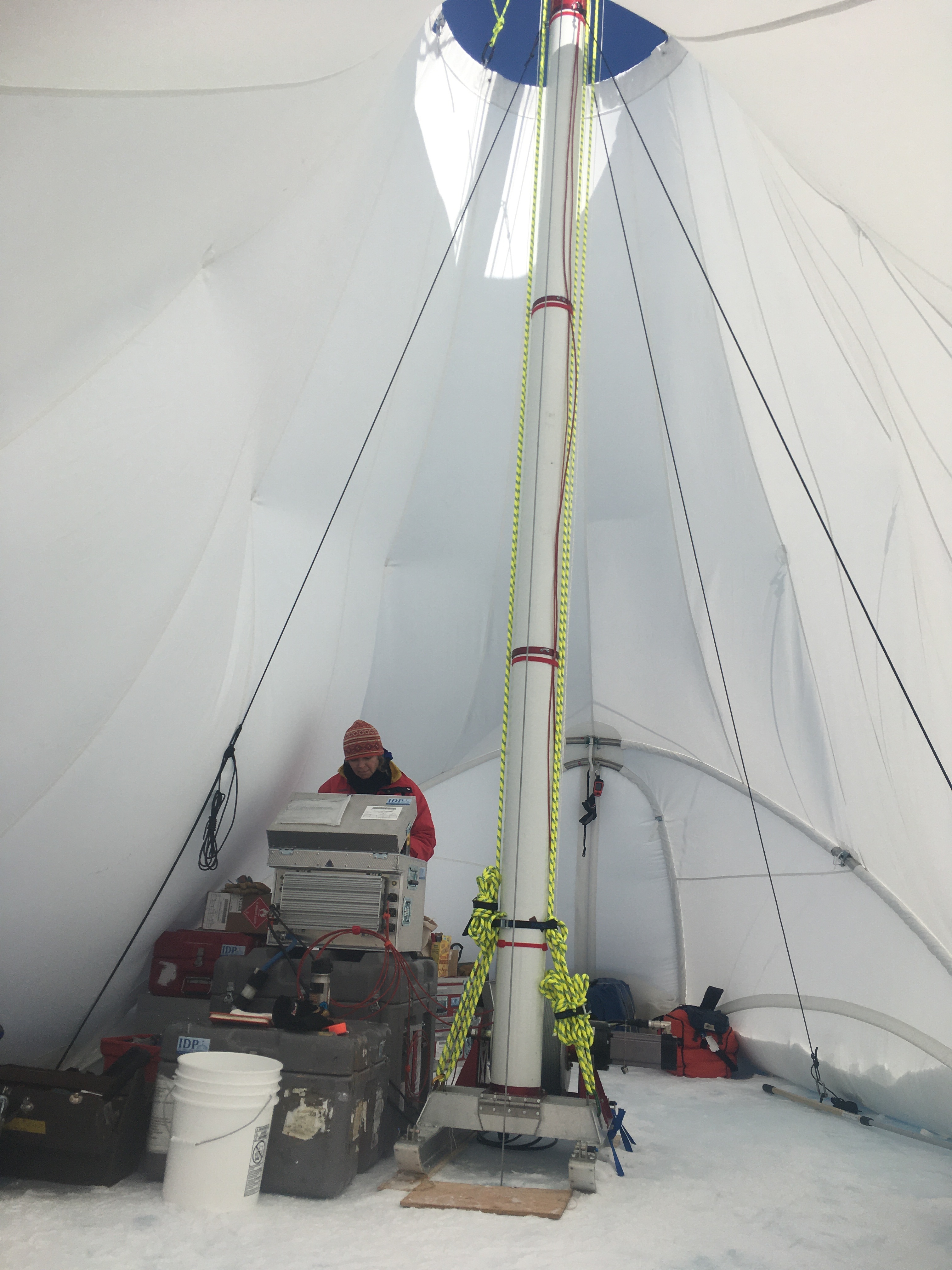
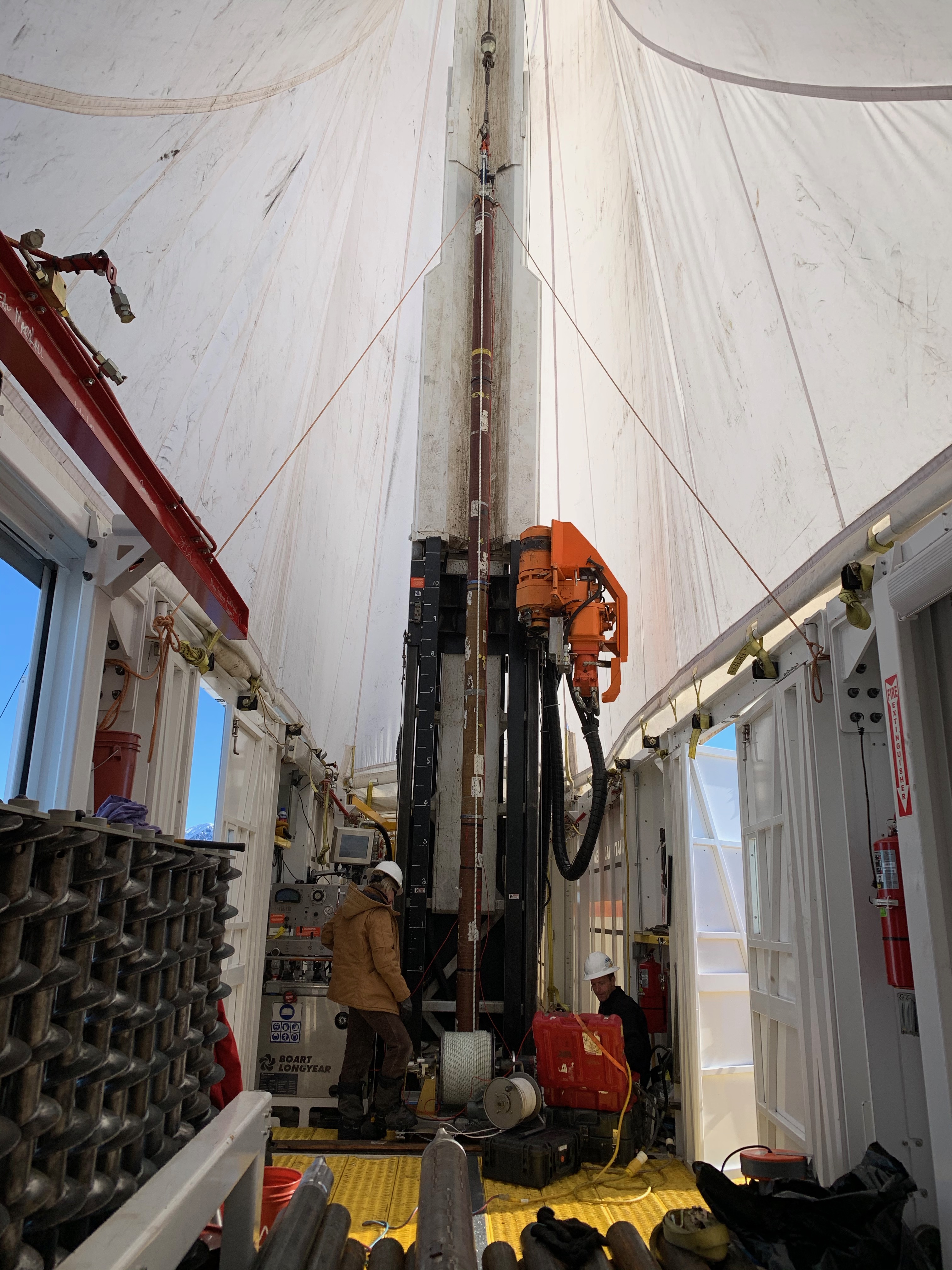
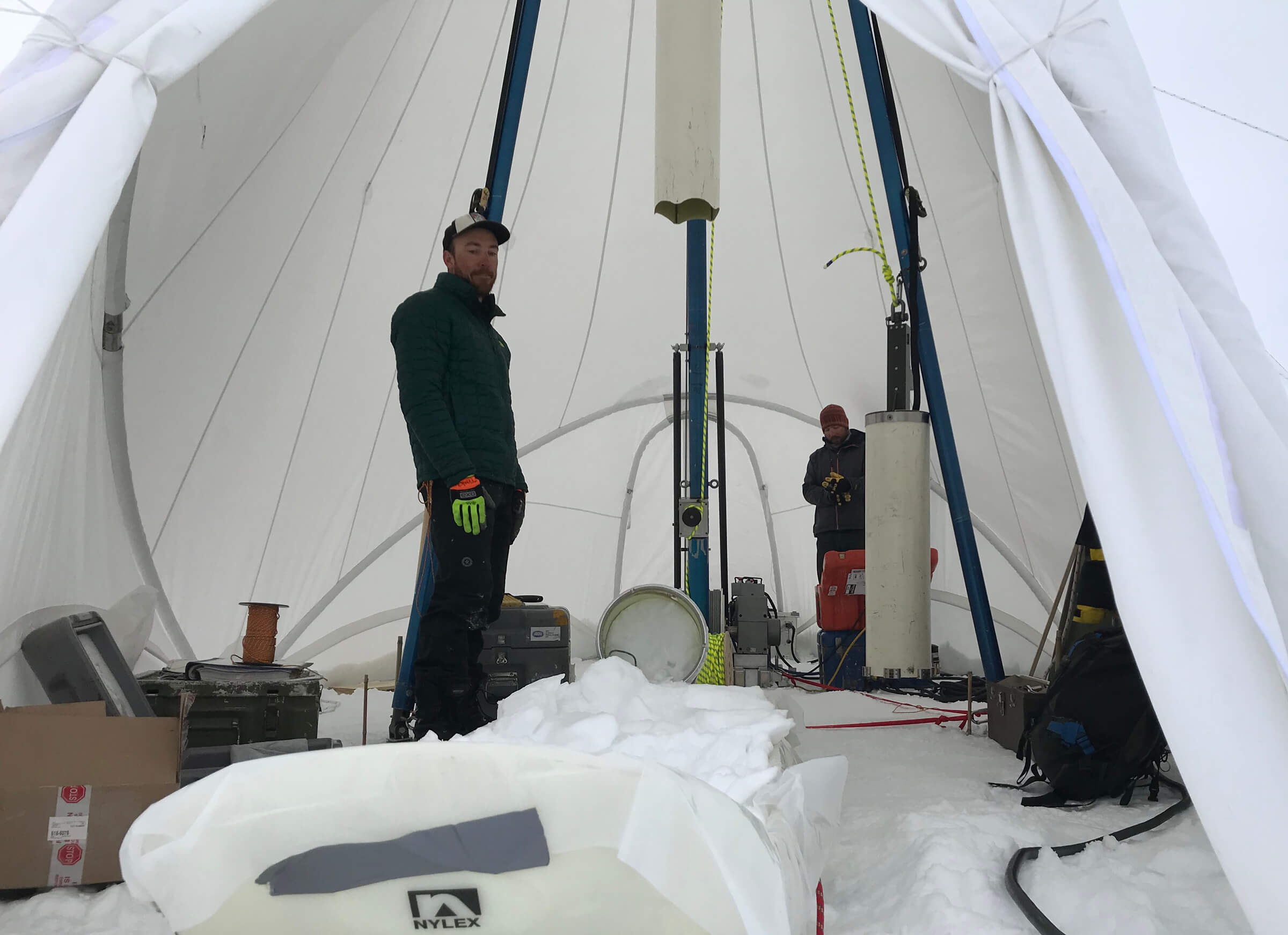
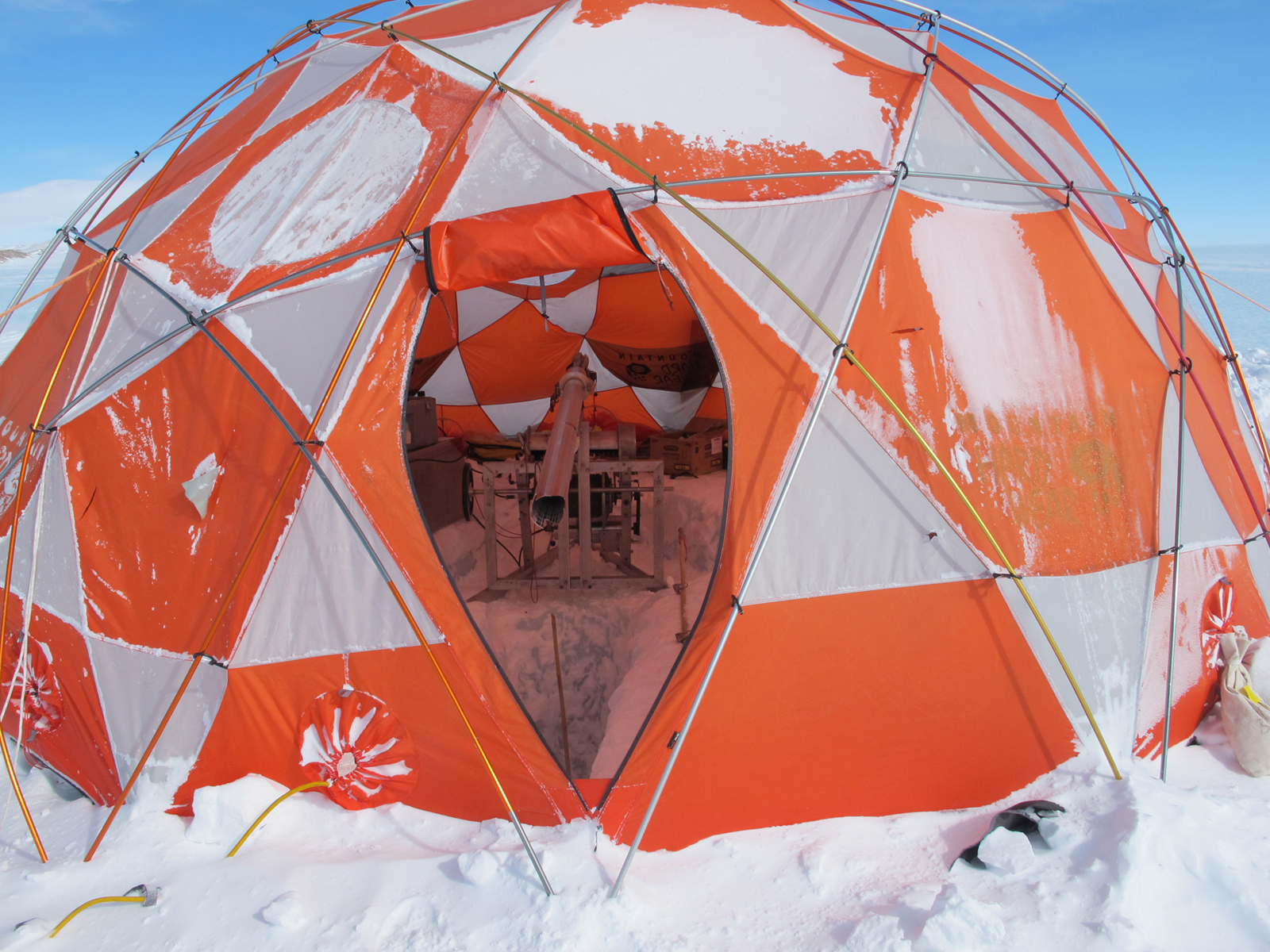
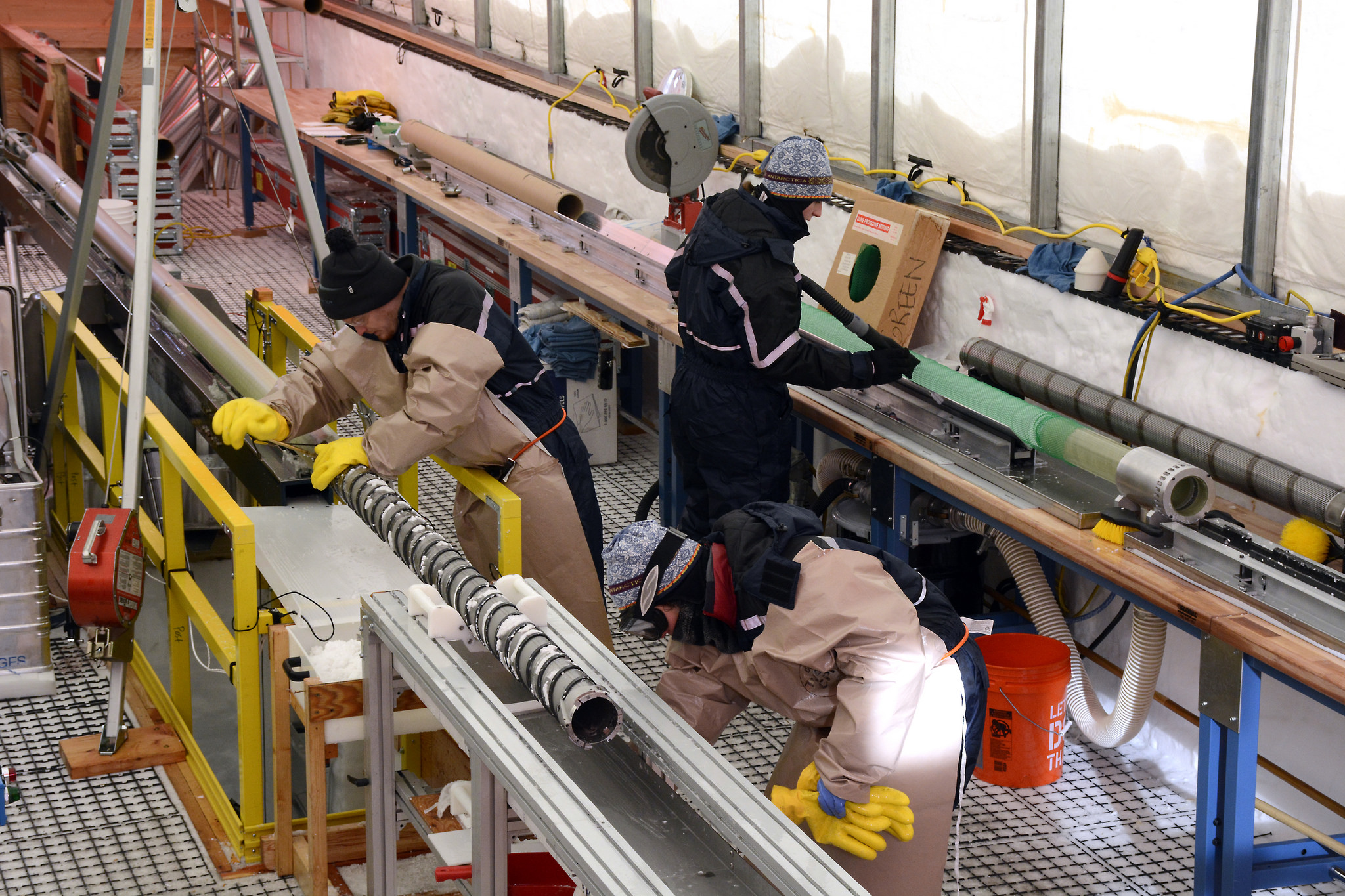
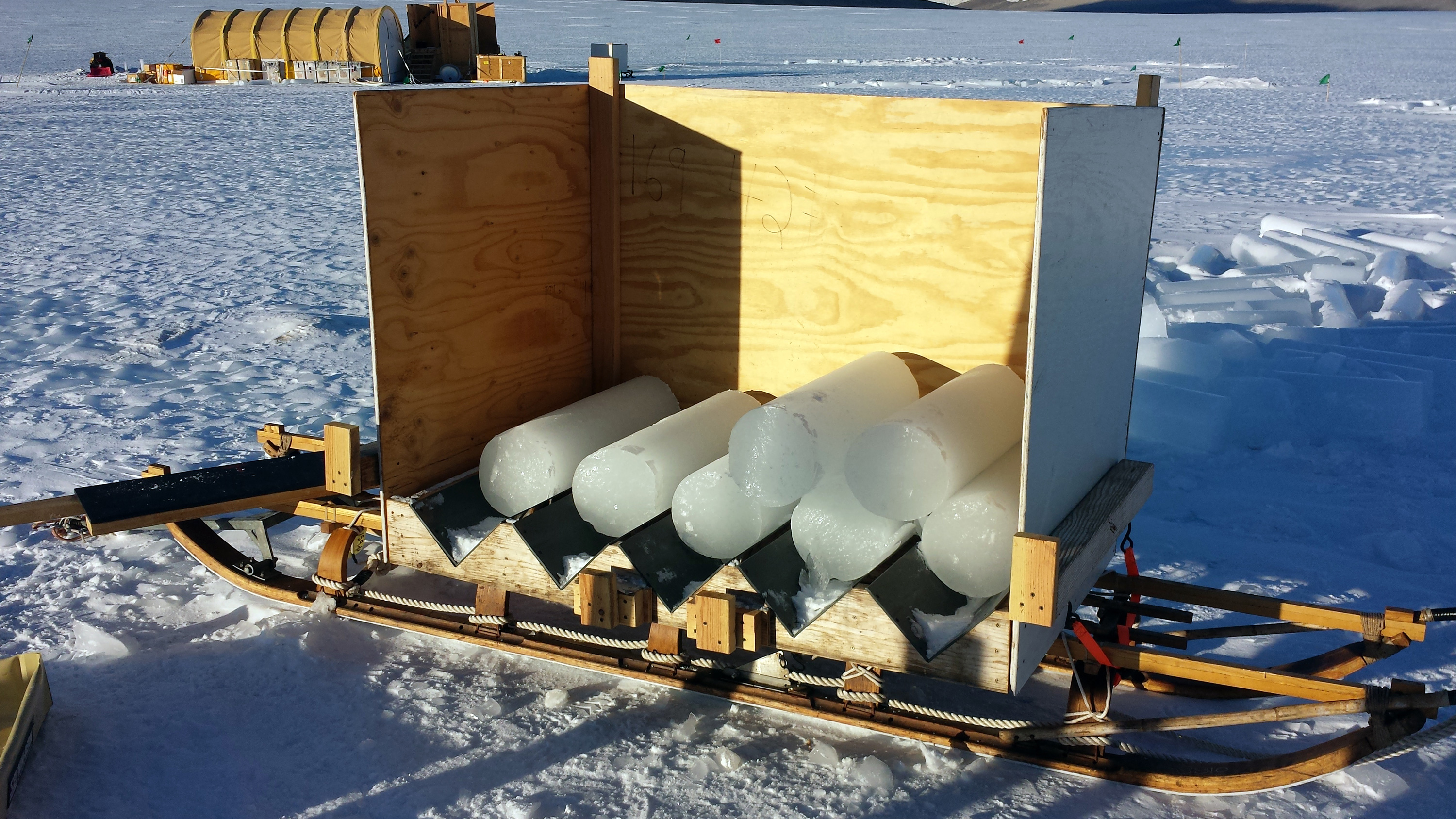
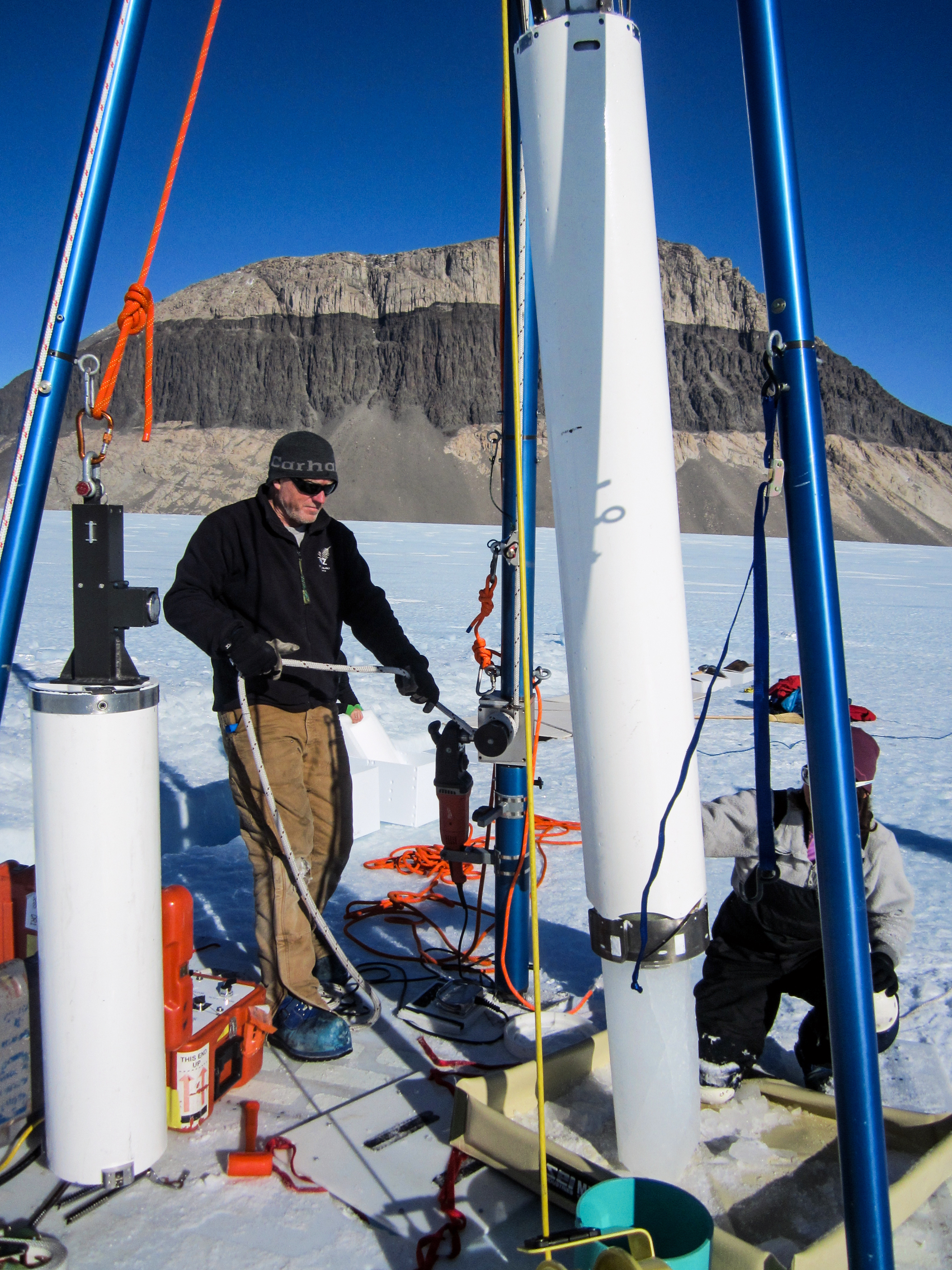
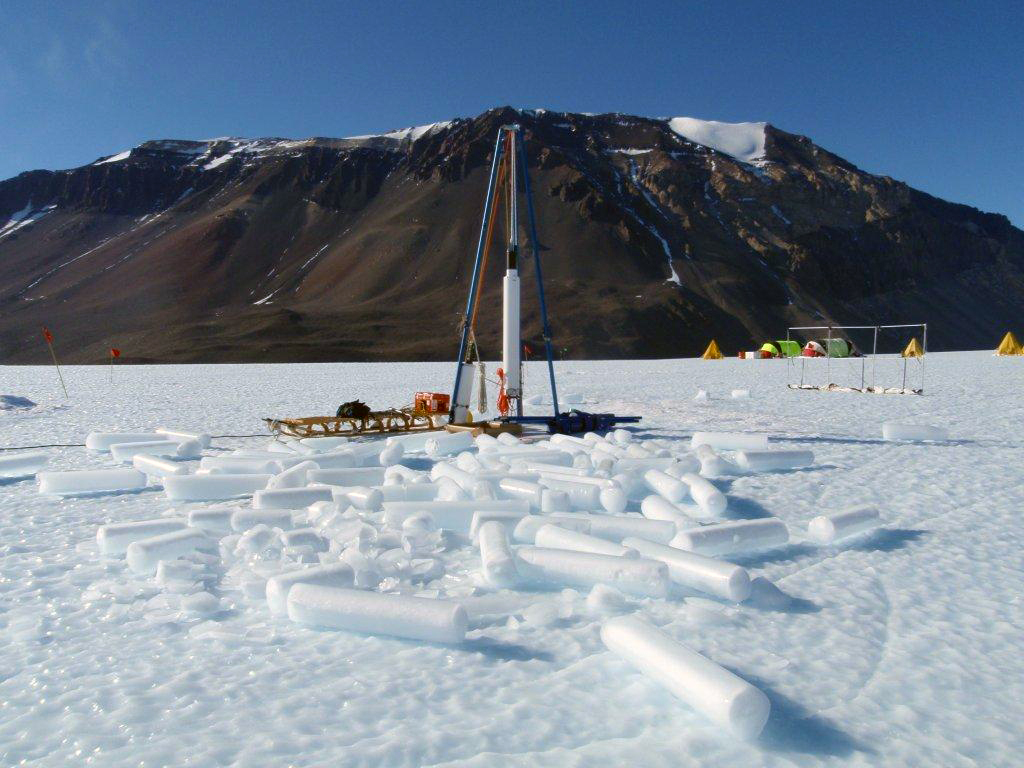
Over the summer, the IDP team worked to repair and maintain several drill systems, many of which will be deployed during the upcoming 2025/26 Antarctic field season. A penetration drive and a load cell were added to the Blue Ice Drill to provide the operators with finer control and more feedback, and a new steel core barrel was fabricated, along with large quantities of carbide cutter inserts. These modifications are an effort to improve core quality in the challenging ice conditions encountered at Allan Hills and beyond. The team also worked to develop the Shallow Wet Drill, which is not a new, standalone drill per se, but features the combining of several components from existing drills in inventory (e.g. Foro 400 anti-torque sections, Foro 1650 motor sections, 700 Drill winch/tower/tent, etc.) with new core barrel components to assemble a drill for testing shallow wet drilling operations at Allan Hills. IDP also designed and is fabricating several tower lifting fixtures to increase safety during the field operation of raising drill towers. IDP anticipates deploying 8 team members for the upcoming field season. In early September, 26 pallets and 16,000+ pounds of equipment departed Madison for Port Hueneme, CA, where it will travel to either Christchurch, New Zealand, or Punta Arenas, Chile, via ship.
Blue Ice Drill
IDP Gears Up for the Antarctic Season
Blue Ice Core Quality Feasibility Study
Drilling in ice without the use of a borehole fluid can be achieved to depths of 300-350 meters before risking borehole closure. However, the ice cores extracted from depths exceeding 150-180 meters often exhibit very poor core quality. IDP has largely found this to be true, except when drilling at the Allan Hills in Antarctica, a Blue Ice Area (BIA), where core quality deteriorates at depths as shallow as 50 meters. The exact reasons for this deterioration in core quality at shallower depths in BIAs compared to non-BIAs are not fully understood.
In IDP’s 2024 Long Range Science Plan, IDP was tasked with conducting an engineering feasibility study to evaluate and recommend long-term drilling approaches for retrieving high-quality ice cores down to a depth of 400 meters in BIAs. In a new report, IDP outlines several solutions proposed to improve core quality in BIAs, along with the advantages and disadvantages of each. The report also discusses how core quality is defined, the past performance of IDP’s shallow drills, and lessons learned from drilling in non-BIAs. For more information, read the Blue Ice Core Quality Feasibility Study.
Drill Maintenance and Testing in Full Swing at IDP-WI
IDP engineers worked efficiently during the second quarter to repair and test equipment returned from Antarctic field projects before quickly shipping the equipment to Scotia, NY, for projects in Greenland.
IDP Supports a Successful 2019/20 Antarctic Field Season
The 2019/20 Antarctic field season was a bustling time for IDP. The entire engineering staff of IDP deployed across five different sites. Using the Winkie Drill and Badger-Eclipse Drill, Engineer Grant Boeckmann and Research Intern Elliot Moravec successfully collected four subglacial rock cores on Thwaites Glacier in the Hudson Mountains for PI Brent Goehring’s project. Engineer Tanner Kuhl and Driller Elizabeth Morton supported PI John Higgins’s work at Allan Hills through operation of the Blue Ice Drill and the new Foro 400 Drill. IDP Warehouse Manager Jim Koehler operated the Intermediate Depth Logging Winch (IDLW) at South Pole Station in support of PI Kael Hanson’s logging of the SPICEcore borehole and then transitioned to WAIS Divide to assist Engineer Chris Gibson with testing of the new RAM 2 Drill components with the original RAM Drill compressors. They were also able to perform brief testing on the Small Hot Water Drill, which will serve as the backup drill for PI Sridhar Anandakrishnan’s GHOST project on Thwaites Glacier in 2020/21. Engineer Jay Johnson deployed to Minna Bluff with the RAID project at the request of PI John Goodge and the NSF. In addition to consulting on operation of the RAID equipment, Johnson also used an IDP 4-Inch Drill and chips bailer to assist in setting the RAID packer. He also re-terminated the IDLW cable following damage at South Pole and was assisted in this effort by Kuhl and Morton. The IDLW was then operated in two RAID boreholes by RAID and IceCube personnel. Despite substantial weather and aircraft delays program-wide, objectives were largely completed for all projects, and feedback received from PIs has been very positive.
Field Support to Antarctic 2019-2020 Projects
IDP is providing support to the following projects during the 2019-2020 Antarctic field season:
(1) The Geological History Constraints on the Magnitude of Grounding Line Retreat in the Thwaites Glacier System project (PIs Goehring, Balco, Hall, Campbell; C-443-M; NSF award 1738989) contributes to the joint initiative launched by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the U.K. Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) to substantially improve decadal and longer-term projections of ice loss and sea-level rise originating from Thwaites Glacier in West Antarctica. The goal of the project is to obtain geological evidence from the Thwaites-Pine Island Glacier system that will show whether glaciers were less extensive than they are at present, and, if so, when. The project will utilize the Badger-Eclipse Drill and Winkie Drill to obtain subglacial bedrock from sites where ice thickness is dynamically linked to grounding-line position in the Thwaites system (specifically in the Hudson Mountains). Observation of significant cosmogenic-nuclide concentrations in these samples would provide direct, unambiguous evidence for past episodes of thinning linked to grounding-line retreat as well as constraints on their timing and duration.
(2) The Thwaites-Amundsen Regional Survey and Network (TARSAN) integrating atmosphere-ice-ocean processes affecting the sub-ice- shelf environment project (PI Pettit; C-445-M/N; NSF award 1738992) contributes to the joint initiative launched by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the U.K. Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) to substantially improve decadal and longer-term projections of ice loss and sea-level rise originating from Thwaites Glacier in West Antarctica. Thwaites and neighboring glaciers in the Amundsen Sea Embayment are rapidly losing mass in response to recent warming and related changes in ocean circulation. The processes driving the loss appear to be warmer ocean circulation and changes in the width and flow speed of the glacier, but a better understanding of these changes is needed to refine predictions of how the glacier will evolve. One highly sensitive process is the transitional flow of glacier ice from land onto the ocean to become a floating ice shelf. This flow of ice from grounded to floating is affected by changes in air temperature and snowfall at the surface; the speed and thickness of ice feeding it from upstream; and the ocean temperature, salinity, bathymetry, and currents that the ice flows into. The project team will gather new measurements of each of these local environmental conditions so that it can better predict how future changes in air, ocean, or the ice will affect the loss of ice to the ocean in this region. The project will use a 400-meter winch with tower and sheave from the 4-Inch Drill as an instrument installation winch to lower instruments into hot water-drilled boreholes on the Dotson Ice Shelf to measure ocean water properties at locations where warm Circumpolar Deep Water reaches the Thwaites grounding line.
(3) The Collaborative Research: Snapshots of Early and mid-Pleistocene Climate and Atmospheric Composition from the Allan Hills Blue Ice Area project (PIs Higgins, Brook, Severinghaus, Mayewski; I-165-M; NSF award 1744993, 1745006, 1744832 and 1745007) will collect new ice cores from the Allan Hills Blue Ice Area. Bubbles of ancient air trapped in ice cores have been used to directly reconstruct atmospheric composition, and its links to Antarctic and global climate, over the last 800,000 years. Previous field expeditions to the Allan Hills Blue Ice Area, Antarctica, have recovered ice cores that extend as far back as 2.7 million years. These ice cores extend direct observations of atmospheric carbon dioxide and methane concentrations and indirect records of Antarctic climate into a period of Earth’s climate history that represents a plausible geologic analogue to future anthropogenic climate change. Through this project, the team will return to the Allan Hills Blue Ice Area to recover additional ice cores that date to 2 million years or older. The new Foro 400 Drill and Blue Ice Drill will be used to recover the ice cores. The climate records developed from these ice cores will provide new insights into the chemical composition of the atmosphere and Antarctic climate during times of comparable or even greater warmth than the present day.
(4) The Phase 2 Development of a Rapid Access Ice Drilling (RAID) Platform for Research in Antarctica project (PI Goodge; D-551-M, D-552-M; NSF award 1419935) will initiate its third Antarctic Field Trial (AFT3) of the RAID drill system – to collect ice and rock samples from a deep ice sheet near Minna Bluff. The RAID drilling system will be put through a complete set of drilling trials, including augering firn, setting a borehole packer, drilling about 600 meters of grounded ice, and obtain samples of ice and rock cores at depth (by wireline rotary coring). All components of the drilling system will be tested and evaluated. The 4-Inch Drill will be used to make 2-3 meters of smooth-walled borehole just below the firn-ice transition, at a depth of approximately 70 meters, to field test the setting of the borehole packer. The Intermediate Depth Logging Winch will be used to field test a borehole dust logger in selected boreholes produced this season at Minna Bluff.
(5) The Management and Operations of the IceCube Neutrino Observatory 2016-2021 project (PIs Halzen and Hanson; A-333-S; NSF award 1600823) will utilize the Intermediate Depth Logging Winch to lower a series of optical+UV and radio sensor packages into the South Pole Ice Core (SPICEcore) borehole to the full depth of the hole (1751 m). The science goals include measurements of the radio absorption length of the ice from 100-1000MHz, radio birefringence in the ice, and ice index of refraction, all measured as a function of depth and ice temperature. The science team is interested in the optical scattering, absorption lengths, and luminescence as a function of depth and optical wavelength from the visible into the ultraviolet.
Successful Support of 2018-2019 Antarctic Law Dome Project
IDP deployed engineers Tanner Kuhl and Grant Boeckmann for the jointly-supported NSF and Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) Law Dome Project. IDP worked for several years with PI Vas Petrenko and the AAD to plan for an ambitious amount of ice coring using three IDP drill systems: a Badger-Eclipse Drill, a 4-Inch Drill, and the Blue Ice Drill. Despite challenging weather conditions, over 1,000 meters of ice core was drilled across six boreholes, surpassing the original science objectives. This project also represented the first deployment of the newly-acquired Blue Ice Drill tent. Project participants report that the tent performed well, even during high winds, allowing for continued operations during inclement weather.
Equipment Updates (2018 Summer)
Foro 3000 Drill
IDDO continued initial development tasks for the Foro 3000 Drill system during the third quarter. Detailed design of the winch drum and level wind are in process. Sizing calculations were made and a design initiated for the chip melter system. Sonde assembly drawings were largely completed. Design work is expected to ramp up in the fourth quarter in preparation for a Detailed Design Review in late September.
Foro Drill
Anti-torque section assembly was largely completed and motor section assembly was initiated on the Foro Drill. Cabling was completed for the control box and drill motors were ordered. Shipping cases were received for the sonde, tower, and winch. Cutter head assemblies, spare cable terminations, and anti-torque slip rings were also received. Some assembly and testing have been delayed in light of work on higher priority projects, but procurements are largely complete.
Rapid Air Movement (RAM) Drill
Continued acceleration of RAM Drill design, procurement, and in-house testing. The system was prepared, packed and shipped to Scotia, NY in late June. In early July, IDDO received an Expedition Permit from the Government of Greenland, and a two-week field test was subsequently completed at Camp Raven in late July.
Intermediate Depth Drill
Models and drawings were completed for the winch cable terminations and spare cable termination kits were received for the Intermediate Depth Drill. System maintenance continues at a slow pace, as does the testing and troubleshooting of the Mage Controls components. The components, returned to Mage Controls at the end of the second quarter, are expected back at IDDO early in the fourth quarter.
Winkie Drill
Borehole casing was specified and purchased in preparation for the Winkie Drill's first use in West Antarctica at a drill site with overlying firn. IDDO sought information from international colleagues regarding methods to seal the bottom of the casing to the ice. Packer components, benchtop testing for compressed air inflation, and detailed models of packer components were also researched.
Blue Ice Drill (BID)
Maintenance and upgrade tasks were largely completed during the quarter for the BID-1. The drill was subsequently cleaned, packed and shipped for the upcoming Law Dome project in Antarctica. IDDO continued communication with BID tent vendor Fabricon. Engineer Tanner Kuhl visited the vendor's location in mid-July to review the design and progress thus far, and the tent was completed in mid-August.
Thermal Drill
The Engineering Requirements document for the Thermal Drill was approved and released. IDDO engineers worked to identify, procure and test some thermal and power limiting materials and components during the quarter. New heat rings were specified, as the old model is now out of production, and a number of new rings were ordered late in the quarter.
Hand Augers
Planned modifications for the cleat and locking break components of the SideWinder units were implemented on all five kits in inventory. Equipment was returned from Svalbard and Greenland and was repaired as needed. Orders were subsequently placed for replacement of a few components that were stuck in the ice during the 2018 Arctic fieldwork.
4-Inch Drills
Maintenance was completed for the 4-Inch Drill system that returned from Antarctica. One core barrel set was modified to match beneficial modifications made to another barrel set in inventory. An improved cable keeper for the crown sheave was designed, fabricated and implemented.
Eclipse Drills
A more robust top cover and new side panels were installed on the Eclipse Drill traversing system. Beneficial updates were made to the Operator's Manual. Small tools such as strap wrenches and sharpening stones were purchased for use in the field.
Antarctic Cargo Preparation Commences for Law Dome Project
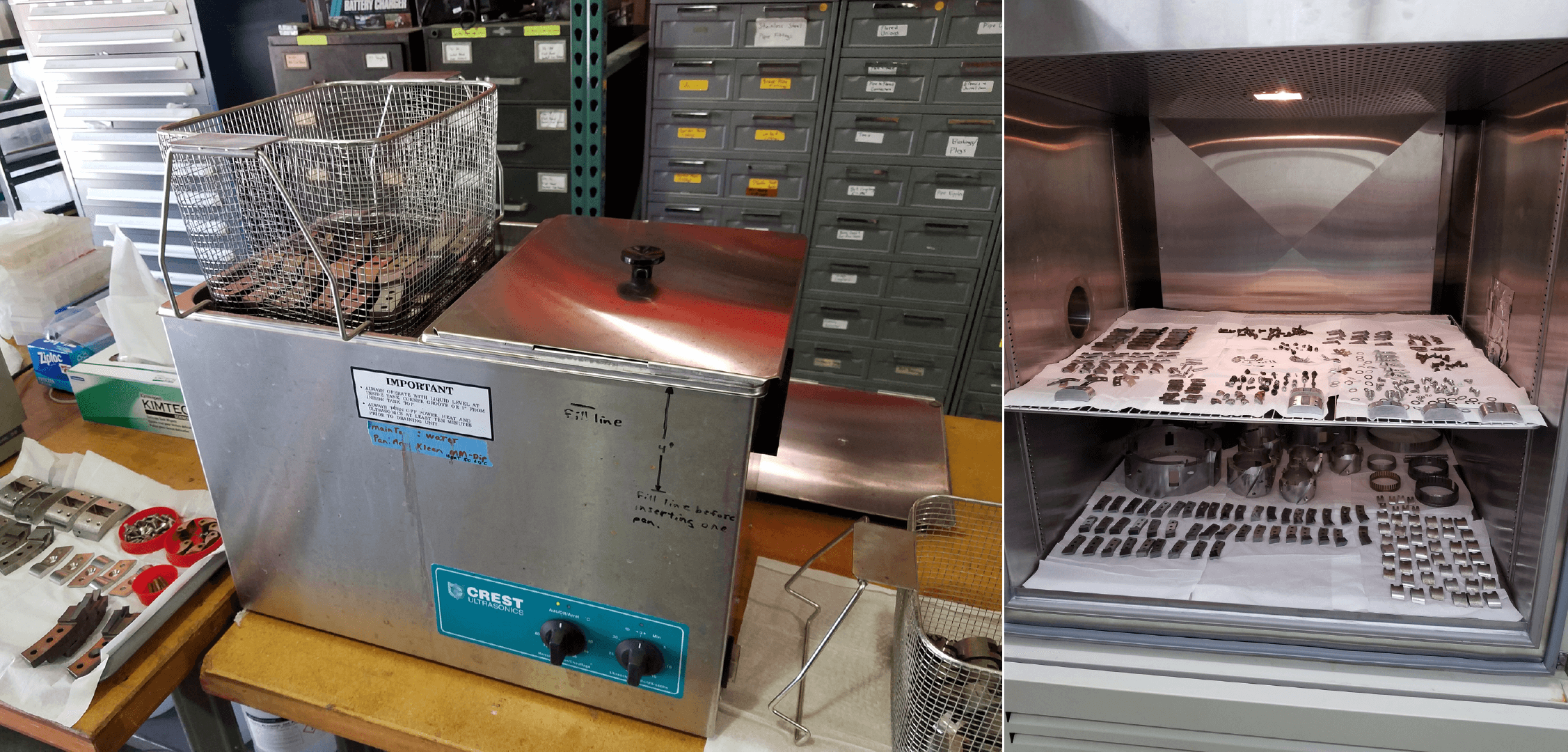
In early June, IDDO turned its attention to cargo preparation for the Law Dome field project (PI Petrenko). IDDO staff have been participating in regular teleconferences with the science team and the Australian Antarctic Division to prepare for the joint U.S.-Australian supported fieldwork. At IDDO, an extensive cleaning protocol was implemented for a 4-Inch Drill, a Badger-Eclipse Drill and the Blue Ice Drill, to ensure carbon-free sampling during the upcoming Law Dome project. Drill parts underwent ultrasonic cleaning in acetone, followed by further cleaning in ethanol and deionized water. Metal parts such as coring heads, cutters, etc. were further baked overnight in an environmental chamber. The cargo was subsequently shipped on July 26, 2018, to Port Hueneme, CA, eventually bound for Hobart, Tasmania.
Equipment Updates (2018 Spring)
Foro 3000 Drill
IDDO continued initial development tasks for the Foro 3000 Drill system during the second quarter. Modifications were made to the Intermediate Depth Drill cutter head design that may make it possible to perform multiple core breaks during one drill run. This will be of value when drilling brittle ice with the Foro 3000 Drill. Detailed design of the winch drum was also initiated during the quarter.
Foro Drill
Fabrication of the Foro Drill core barrels was completed and all parts for the anti-torque and motor sections were ordered except for the actual drill motors for which IDDO expects to pursue quotes in the third quarter. The magnetic slide hammers were assembled, and load testing of the sled and hitch was completed. Shipping cases for the sondes, tower, and winch were also ordered.
Rapid Air Movement (RAM) Drill
Acceleration of RAM Drill design and procurement tasks continued to accommodate a potential test of the system in Greenland during summer 2018. All major component orders have been placed and electrical testing of the sonde was initiated. Initial testing for air pressure losses was completed.
Thermal Drill
Updated science requirements for IDDO's Thermal Drill were finalized at the end of February. A thermal or power limiting feature is being planned as part of the system upgrades, to help prevent premature heat ring failure. A benchtop testing procedure was initiated during the quarter and a number of thermal/power limiting options are under consideration. A manufacturer of suitable heat ring elements has been identified, and a core removal tool was designed and built making use of magnets to disengage the core dogs.
Intermediate Depth Drill (IDD)
The new 1650-meter long winch cable was spooled on the winch drum and was terminated, and the level wind controls were modified to work with the current emergency-stop system. Acceptance testing and troubleshooting of the Mage control system components continued. At the end of the quarter, the IDD's control system components were shipped back to Mage for further tuning.
Winkie Drill
IDDO is pursuing upgrades to integrate borehole casing with the current Winkie Drill system for a planned Thwaites Glacier project. Technology from the rock drilling industry and international ice drilling community is being researched.
Blue Ice Drill (BID)
Redesigned components for the BID tripod feet were received and installed during the quarter. A custom tent enclosure manufacturer was identified in April, and design of a tent and its integration with the BID tripod system has been initiated.
In summer 2017, IDDO worked to begin fabrication of a second BID-Deep system (for wide-diameter ice coring to 200 meters), based on user demand and per a directive in the IDPO Long Range Science Plan 2016-2026. Fabrication of the second system was initially scheduled for completion in Program Year (PY) 2018. However, there is no longer a funded science project this year that requires a second BID-Deep system, and therefore completion of the second BID-Deep system has been postponed to enable work on higher-priority projects in PY 2018.
Foro 700 Drill
The IDPO Science Advisory Board identified in the IDPO Long Range Science Plan 2015-2025 a priority need to alter the surface equipment for the existing Intermediate Depth Drill to make a drilling operation that is less logistically intensive, to be used for ice coring at sites with limited logistics and with two months or less time on site. From discussions organized by IDPO with iterative discussions between IDPO, scientists, and IDDO staff, the science requirements for a 'Foro 700 Drill' were completed during the second quarter. The next step is to develop the conceptual design for the drill, which could possibly happen in PY 2019 pending availability of funds and project prioritization.
Successful Support Across Antarctica
Several other projects supported by IDPO-IDDO were also successfully brought to a close during the quarter. Drilling efforts for the cosmogenic C-14 project on Taylor Glacier were completed for the third and final year. Out at Allan Hills, an IDDO driller utilized an Eclipse Drill to successfully core three holes to bedrock, collecting precious ancient ice. A second Eclipse Drill project was completed at South Pole Station. Finally, after years of programmatic delays, IDDO was able to conclude its operations related to use of the DISC Drill at WAIS Divide. All equipment is now disassembled, packed, labeled and ready for return to the U.S. as flights allow. IDDO also successfully extended the borehole casing to allow for future logging operations, including planned logging during the 2016-2017 field season.
South Pole Ice Core (PI Aydin)
An IDDO team of seven engineers and drillers, led by Lead Driller Jay Johnson, successfully completed this two-year drilling endeavor at South Pole Station, achieving a final borehole depth of 1751 meters, 251 meters beyond the original goal of the project. All necessary retro cargo was readied for vessel and COMAIR transport back to the U.S., whereas the drill tent and other items were winterized for use again in 2016-2017.
WAIS Divide Deep (PI Albert)
IDDO Driller Jim Koehler arrived at WAIS Divide on 1/14/16, following weather and aircraft delays, and worked expediently to prepare the remaining DISC Drill items for return shipment to the U.S. Koehler also worked with ASC personnel to extend the borehole casing to two feet above the Arch floor level.
Taylor Glacier Blue Ice Cores (PI Petrenko)
IDDO Driller Mike Jayred operated the Blue Ice Drill (BID) in support of PI Vas Petrenko's C-14 of atmospheric methane fieldwork at Taylor Glacier. All science samples were successfully collected, with over 480 meters of core drilled over 35 drilling days. In total, over 40 holes were completed through approximately 530 drill runs. IDDO support of this three-year project is now concluded.
Climate Controls on Aerosol Fluxes in Taylor Valley (PI Aciego)
IDDO Driller Mike Jayred operated the Blue Ice Drill (BID) in support of PI Sarah Aciego's aerosol fluxes fieldwork at Taylor Glacier. All science samples were successfully collected in early November 2015, with 20 meters of core collected during this short duration project.
Allan Hills (PI Higgins)
IDDO Driller Mike Waszkiewicz operated an IDDO Eclipse Drill at Allan Hills in support of PI John Higgins' ancient ice fieldwork. All science samples were successfully collected. Each of the two planned holes were drilled to bedrock, with the first hole drilled to a depth of 100 meters and the second hole to a depth of 205 meters. The team was also able to re-enter a third hole that was originally drilled in 2011, coring an additional 20 meters of what is believed to be million year old ice.
South Pole Firn Air (PI Sowers)
Trevor Popp, an American driller and scientist working at the Centre for Ice and Climate in Copenhagen, Denmark, operated an IDDO Eclipse Drill at South Pole in support of PI Todd Sowers' firn air sampling campaign. In early November 2015, Popp set up the drill and began drilling without incident. Firn air sampling was progressing well until the firn air bladder provided by and operated by the science team became stuck in the borehole at 100 meters depth. Following unsuccessful efforts by the science team, IDDO, and ASC to retrieve the firn air sampling equipment, the hole was abandoned and efforts were redirected to drilling of the second hole, which was successfully drilled to 128 meters. Core quality was excellent throughout and the penetration rate was exceptional.
Hand Augers
During the 2015-2016 Antarctic field season, IDDO supported ten investigators through the deployment of a variety of hand auger and Sidewinder kits. The hand auger kits are currently en-route back to the U.S. via the cargo vessel.
Crary Ice Rise Shot Holes (PI Conway)
IDDO supplied PIs Twit Conway and Paul Winberry with a Small Hot Water Drill to create shot holes for their Crary Ice Rise seismic work. All shot holes were successfully drilled by the science team, and the equipment is currently onboard the cargo vessel headed to the U.S.
Exposed Rock Beneath the WAIS (PI Stone)
In anticipation of the upcoming 2016-2017 fieldwork, IDDO shipped borehole casing and drill rod for the ASIG Drill to Antarctica via the resupply vessel. These items are planned for use during the 2016-2017 field season to support PI John Stone's fieldwork near Pirrit Hills. The borehole casing and drill rods were shipped early to reduce ASC's shipping costs and to allow the cargo to be flown to West Antarctica in 2016-2017 on flights of opportunity.
Equipment Development (2015 Summer)
Agile Sub-Ice Geological Drill
Purchasing efforts ramped up for the Agile Sub-Ice Geological (ASIG) Drill project. A web/teleconference review of the Integrated Detailed Final Design was held on May 28, 2015 with participation from IDPO, IDDO and SSEC engineers and several experts and colleagues from various drilling industries. Project Manager Chris Gibson worked with the manufacturer of the base rig (Multi-Power Products Ltd. in British Columbia, Canada) to resolve issues identified in Madison during initial Acceptance Testing. The manufacturer has subsequently completed all rework of system components that did not originally meet the weight specifications outlined in the contract. Planning efforts have increased for the upcoming test of the drill's packer device (for sealing the borehole casing to non-porous ice) near McMurdo Station during February 2016, and for the larger-scale ASIG Drill system test planned in Madison, WI, during the upcoming winter.
Intermediate Depth Drill
Preparation is well underway for the second production season of the SPICEcore project at the South Pole. A new drill motor was purchased to replace one that sustained damage during the 2014-2015 field season. Work was performed to repair, standardize and test all circuit boards in the control system. Maintenance and repairs were initiated for the chip chamber, chip valve, hollow shaft assembly, pump and anti-torque slip sensor. Repair of the tower pendant was completed, with the addition of Teflon cabling for durability during contact with drill fluid. A power meter was also specified and parts for it were ordered. IDDO plans to ship all repaired and modified Intermediate Depth Drill equipment back to the South Pole in mid-September.
Blue Ice Drill – Deep
Engineers monitored the progress of new cutters deployed for testing in Greenland, in an effort to improve Blue Ice Drill – Deep (BID–Deep) core quality. The drill was able to drill to approximately 155 meters using the new step cutters and trying a variety of other techniques before core quality was no longer acceptable. This is approximately 15 meters deeper than the prior year, but still short of the initial 200 meter depth goal. Interactions with the IDPO Science Advisory Board will determine if additional efforts should be made for quality core at greater depths.
Winkie Drill
IDDO received approval from IDPO to pursue purchase of a commercially available Winkie Drill from Minex. Following telecons with IDPO, NSF and Ohio Range project PIs Robert Ackert and Sujoy Mukhopadhyay, IDPO-IDDO determined purchase of this new rock coring drill would better serve the needs of the Ohio Range project to obtain rock samples from the ice-bedrock interface, and the larger community, as opposed to making repairs and modifications to the Koci Drill. The new Winkie Drill is also expected to prove useful for the joint RAID/ASIG auger and packer tests near McMurdo in February 2016. Necessary purchase orders have been submitted. Upon receipt of the rig, IDDO will make modifications to the Winkie Drill to expand its capabilities to include augering and coring through ice.
Continued Success on Taylor Glacier
On Taylor Glacier in the Dry Valleys region, driller Mike Jayred successfully drilled over 930 meters of large-diameter ice cores for PIs Vas Petrenko, Ed Brook and Jeff Severinghaus using the IDDO Blue Ice Drill. Over 1,000 drill runs were completed and 52 holes were drilled. Cores were again melted onsite for in-field gas analysis. The Blue Ice Drill is now being returned to Madison for minor repairs, cleaning, and re-packing prior to its use in Greenland in May.
Cosmogenic Carbon-14 Core Project Successfully Completed Following Early Season Challenges
During the recent Arctic field season, IDDO again supported PI Vas Petrenko's Carbon-14 sampling efforts outside of Summit Station, Greenland using IDDO's Blue Ice Drill (BID). Despite early season challenges that saw one of the two IDDO drillers and three of Petrenko's science technicians returned home for medical reasons, the team rebounded during the following flight period. With assistance from additional science technicians and help from IDDO drillers already in Greenland for the IDD test, the team was able to successfully complete all drilling and sampling objectives. The large-diameter ice cores drilled by the BID were again melted onsite for in-field gas analysis. In addition to the use of the base BID system, IDDO also tested components of the new BID-Deep system, which will enable the drill to reach depths down to 200 meters. This testing was in preparation for a related project being conducted by Petrenko in the Dry Valleys region of Antarctica. BID-Deep testing resulted in the drilling of a 187 meter borehole. Core quality was found to be an issue after approximately 140 meters, however IDDO engineers were able to determine that the fabrication of less aggressive cutters should substantially improve core quality at these depths in the future. Over the course of the season, a total of 59 holes were drilled over 26 days of drilling. 1258 meters of core were recovered in a total of 1151 drill runs. The drill was returned to Madison in mid-July, where it was repaired and subsequently shipped to Antarctica in late August.
In addition to the large field projects supported by IDDO in Greenland, IDDO also provided hand auger and Sidewinder equipment to PI David Noone for the fourth and final season of his four-year field project. All equipment was returned to Madison for repair and cleaning following the field work. Another project in Northwest Greenland, PI Erich Osterberg completed shallow drilling outside of Thule Air Base, also using IDDO hand auger equipment. That equipment is in the process of being returned to Madison on flights of opportunity out of Thule.
Late in the third Quarter, in addition to all of the drill system repairs and modifications going on, IDDO also looked toward the upcoming Antarctic season, working with the Berg Field Center (BFC) in McMurdo as well as with PIs to plan for a variety of hand auger projects during the upcoming austral summer. IDDO also initiated the hiring process for the SPICE Core project, to be conducted at the South Pole using the Intermediate Depth Drill, and for the WAIS Divide Ice Core project, in which the DISC Drill will be fully disassembled and packed for return to the U.S.
New Technology for the Community (2014 Spring)
New Generation of an Intermediate Depth Drill
In the second quarter of PY 2014, IDDO completed the building, final testing, and integration and troubleshooting of the Intermediate Depth Drill (IDD) system. By April 15th, the entire IDD drill had been packed and shipped to Greenland for field testing. In spite of the extra effort needed for the building, testing and troubleshooting of four newly developed electronic boards and the electrical failure of the new Sorensen 600V Power Supply during the final testing, all equipment was fully tested and shipped to Greenland on time. The IDD drill will be used for PI Eric Saltzman's two-year South Pole Ice Core project (SPICE Core) during the 2014-15 and 2015-16 field seasons.
New Blue Ice Drill-Deep System
IDDO completed the building, final testing and integration, along with troubleshooting, of the new BID-Deep system. This new drill is a modification of the base Blue Ice Drill (BID) and has the capability of reaching depths of 200 meters. Final testing and packing was completed by the end of April, and the BID-Deep was shipped to Greenland in May for field testing. The base BID will be used on PI Vas Petrenko's project 10 km north of Summit.
Deep Logging Winch
The new IDDO Deep Logging Winch system, capable of logging to depths of 4,000 meters, is completely built, tested, packed, and ready for future field projects. The list of necessary spare parts is created, but the spares will not be purchased until a project utilizing the winch is funded.
"Clow" Deep Logging Winch
During the Second Quarter, the deep logging winch designed, built and operated by Gary Clow was transferred from the U.S. Geological Survey to IDDO. The winch is currently in Antarctica and will be used for the logging of the WAIS Divide deep borehole during the 2014-2015 field season. IDDO anticipates that the logging winch will be returned to Madison, inspected and repaired as necessary prior to use on any future projects.
Scalable Hot Water Drill
The science requirements for the Scalable Hot Water Drill (ScHWD) were completed in late February after several iterations between IDPO-IDDO and the scientists interested in the development of the drill. Engineering requirements based on the science requirements were completed by IDDO. The conceptual design of the ScHWD is nearly complete and an internal review of the drill concept was conducted in mid-May. An outside review of the drill concept will be conducted in early summer.
Agile Sub-Ice Geological Drill
Good progress was made on the Agile Sub-Ice Geological (ASIG) Drill during the Second Quarter with the science requirements being finalized in early February. The science requirements were the result of an iterative process between IDPO, IDDO and scientists interested in the drill, as with the SHWAD. Bill Eustes visited IDPO-Dartmouth in March, where discussion issues with Albert and engineer Tanner Kuhl included aspects of the sub-ice geologic drill development. Albert traveled to IDDO in March to participate in IDPO-IDDO discussions with representatives from Sandvik. Finalization of the concept for the drill, which will be designed to drill through up to 700 meters of ice and then retrieve a small diameter rock core 10-meters long, and review of the concept will take place this summer when Tanner Kuhl returns from Greenland.
Changing Seasons for Field Project Support: Wrapping up a Successful Antarctic Season and Readying for a Bustling Arctic Season
The second quarter (February 1, 2014 - April 30, 2014) saw several Antarctic projects closed out, with final End-of-Season Reports submitted for the Blue Ice Drill's work on Taylor Glacier and for a successful first deployment of IDDO's new Intermediate Depth Logging Winch at Siple Dome. Later in the quarter, IDDO also worked hard to compile and review information for three Support Information Packages for the following 2014-2015 Antarctic field season.
Substantial efforts during the second quarter brought the final setup of IDDO's new Intermediate Depth Drill (IDD) to life. The majority of the equipment was shipped to Scotia, NY by the end of March, with certain critical components shipped shortly after. A team of six drillers completed the PQ process, and all travel arrangements for their deployment were made. The drillers deployed to Scotia on April 21, but were returned home on April 24, due to a mechanical issue with the LC-130 Hercules fleet. IDDO worked with the NSF, CH2M HILL Polar Field Services and the 109th Air National Guard to weigh options for an abbreviated test season and on April 30, the last day of the quarter, IDDO received a call that the northbound Greenland flights were back on. The IDDO crew made it to Summit, Greenland, on May 6 and had the first core drilled at the Isi test site on May 14. The testing of the Intermediate Depth Drill (in Greenland) is now finished. The last core was drilled on Saturday, May 31. The final depth of the test borehole is 285.3 meters. The drillers are now working on packing to prepare the first round of cargo for a flight to Kangerlussuaq on June 4. The remainder of the cargo is scheduled to fly to Kangerlussuaq on the June 10 flight. The drill team was able to complete all desired tests except for the brittle ice drilling test, due to the Hercules issue delaying the start of the field season.
IDDO continued monthly teleconferences with ASC and the SPICEcore PIs in preparation for the IDD's deployment to the South Pole in November 2014. In addition, engineer/ driller Tanner Kuhl attended the 2014 SPICE Core Planning Meeting at the University of California-Irvine.
IDDO worked with NSF, ASC and the dedicated cargo personnel in Scotia, NY to expedite the return of the Blue Ice Drill (BID) system to Madison after vessel-loading issues in McMurdo threatened to delay the return of much of the Antarctic cargo. The BID was needed in Madison in order for IDDO to implement new BID-Deep components and turn the system around for the upcoming Arctic field season. By the end of April, all cargo was packed for PI Vas Petrenko's upcoming project at Isi Camp, and driller Mike Jayred and engineer/driller Josh Goetz were PQed. Jayred and Goetz subsequently deployed on May 11.
IDDO also prepared for a few upcoming hand auger projects in Greenland. Kits were packed and shipped for PI Sarah Das, who used one of IDDO's new 3-Inch hand auger kits to drill shallow cores at one site on Disko Island and at two sites on the Nussuaq Peninsula in late April. A hand auger and Sidewinder kit were packed and shipped for PI Erich Osterberg, who plans to drill cores up to 40 meters depth outside of Thule airbase in late May. Initial preparations were also made for the packing and shipping of hand auger and Sidewinder equipment for PI David Noone's project at Summit Station. Noone's field work in late June and early July will mark the fourth and final year of his four-year project. One additional hand auger project was completed early in the quarter for PI Mike McKay at Bowling Green State University. McKay utilized a new IDDO hand auger to collect river and lake ice samples in the Midwest US as well as in Canada. His project, funded through the NSF Division of Environmental Biology, is scheduled to continue into 2016.
In addition to field season planning and cargo preparation, IDDO also completed proposal support estimates for thirteen separate science projects for the 2014 NSF Antarctic Proposal solicitation. Letters of Support and Cost Estimates were provided to PIs for inclusion in their proposal submissions.
Equipment Development (2013 Winter)
Deep Logging Winch
In the first quarter of PY 2014 (Nov-Jan), IDDO completed the building and testing of a new Deep Logging Winch, capable of reaching the depth of 4,000 meters. At the end of the quarter, the logging winch system required only the completion of the shipping container for the logging tower to be ready for shipment to the field.
Intermediate Depth Drill
IDDO is in the final stage of the development of a new Intermediate Depth Drill, capable of producing ice cores to depths of 1,500 meters. In the first quarter of PY 2014, the procurement of all system parts and components was nearly completed. At the same time, most major assemblies, including the tower, the winch, and the sonde were completed and partially tested as well. Completion of several of the electronics modules, however, has lagged as the result of the responsibility for remaining design, fabrication and testing being assumed by contract engineers and a contract technician after the resignation of the IDDO staff electrical engineer last fall. After the completion of the system integration test in Madison in March of 2014, the entire system will be ready for a full field test in Greenland during the spring-summer of this year.
Blue Ice Drill-Deep
The Blue Ice Drill-Deep is a new drill based on the original Blue Ice Drill (BID) with the capability of reaching depths of 200 meters. The design and procurement of all drill parts and components were completed in the first quarter; all major assembly of new subsystems was completed as well. Modifications and repairs to the base BID, the final assembly of the BID-Deep Drill, and the lab testing will be completed after IDDO receives the base BID back from Antarctica. The BID-Deep system will be shipped to Greenland for testing and fieldwork this summer.
Scalable Hot Water Access Drill
In response to community need for a scalable modular hot water access drill in the Long Range Science Plan, IDDO has started work on a modular hot water drill for the community. This drill will be useful for investigating sub-ice shelf mass balance, ice-ocean interactions, grounding zone processes, and other studies. Mary Albert worked with science community representatives Sarah Das, Dave Holland, and Ted Scambos, and with Chris Gibson, IDDO project manager and engineer and Terry Benson, a University of Wisconsin Engineer with hot water drill experience, through an iterative process to define the science requirements for a hot water drill whose size could be scaled to project needs. The Science Requirements for the Scalable Hot Water Access Drill are available at http://icedrill.org/documents/view.shtml?id=1192. Questions or comments should be sent to Mary Albert.
Agile Sub-Ice Geological Drill
One of the goals for development of new drills identified in the IDPO Long Range Science Plan is the need for agile methods for reconnaissance recovery of small rock cores near ice margins. In response to this, IDPO-IDDO has initiated work on a new Agile Sub-Ice Geological Drill capable of coring up to 10 meters of rock core beneath hundreds of meters of ice. The Science Requirements for this drill were developed in an iterative process led by Mary Albert with community representatives John Stone, Jaakko Putkonen, and Ed Brook, and with IDDO engineer Tanner Kuhl. The Science Requirements are available at https://icedrill.org/equipment/agile-sub-ice-geological-drill. IDPO-IDDO is currently investigating partnership with a small minerals exploration drill manufacturer for development of this drill. The first use of this drill is planned for Antarctic field season 2015-2016 for recovery of rock pieces under several hundred meters of ice. Questions or comments should be sent to Mary Albert.
Agile Ice Coring Drill
In response to the need for an ice coring drill for depths between approximately 400-900 m and that is also agile for use in mountain glaciers and areas with limited logistics, IDPO will be working with community members and with IDDO engineers to develop Science Requirements for the drill. Any U.S. community scientist interested in participating in iterative discussions to identify the requirements should contact Mary Albert at Icedrill@dartmouth.edu.
Successful Project Support Amidst an Uncertain Antarctic Field Season
Despite uncertainties surrounding and delays stemming from the government shutdown in Fall 2013, Antarctic fieldwork was successfully completed for IDDO-supported projects.
Taylor Glacier (PIs Aciego and Petrenko)
On Taylor Glacier in the Dry Valleys Region, IDDO driller Mike Jayred and IDDO engineer Josh Goetz successfully collected over 1300 meters of large-diameter ice cores using the Blue Ice Drill. Despite an intensely windy field season, project objectives were achieved for both PI Vas Petrenko and PI Sarah Aciego.
Siple Dome (PIs Bay and Talghader)
Due to the government shutdown, the U.S. Antarctic Program decided against opening WAIS Divide Camp this season. This has delayed borehole logging operations at WAIS Divide by one field season, but is not expected to negatively impact the disassembly and removal of the DISC Drill from the site, which is now scheduled to occur in 2014-2015. Due to the impact of the shutdown on the logging operations planned for WAIS Divide, PIs Joey Talghader and Ryan Bay altered their project plans to complete less logistically-intense logging projects at Siple Dome this season, both of which were originally planned for the 2014-2015 field season. Assisting in their operations were Josh Goetz and driller Elizabeth Morton. Despite severe flight delays and poor weather at Siple Dome, a very successful maiden voyage of IDDO's new Intermediate Depth Logging Winch helped to complete all project objectives.
Beardmore Glacier (PIs Conway and Winberry)
PIs Howard Conway and Paul Winberry utilized a Small Hot Water Drill once again to successfully drill over 100, 25-meter deep holes for seismic research on Beardmore Glacier, completing the second season of their two-year project.
Shallow Hand Auger Drilling (various PIs)
A number of shallow drilling projects were completed by PIs through the use of hand auger kits provided by IDDO, including two PICO hand auger kits, three SIPRE hand augers, two Sidewinder power drive kits and five new IDDO hand auger kits. The newly designed IDDO hand auger kit has shown excellent results thus far and IDDO continues to collect user feedback on the kit's performance.
Equipment Development (2013 Fall)
Intermediate Depth Drill
Assembly of the various drill subsystems are in process for the Intermediate Depth Drill (IDD), and all assembly and preliminary testing of the IDD is expected to be completed on schedule for the field test in Greenland during the spring of 2014. Upon repair/upgrade from the field test, the drill will be shipped to Antarctica for use at the South Pole during the 2014-15 field season.
Deep Logging Winch
The manufacturer (Markey Machinery Co.) delivered the Deep Logging Winch in early September. IDDO personnel are in the process of completing the design of the winch sled and minor modification to the winch control system. The winch is scheduled for completion in early 2014.
Blue Ice Drill-Deep
IDDO is continuing with the development of the Blue Ice Drill-Deep (BID-Deep) system, based on the existing Blue Ice Drill (BID) system. The new system will be aimed at achieving a depth of 200 m and will eventually be used to acquire very large amounts of ice from Taylor Glacier that are needed for the study of cosmogenic carbon-14. The schedule for development is such that the first field test of the BID-Deep will be in Greenland in the summer of 2014.
Shallow Basal Material Recovery Drill
One of the goals identified in the IDPO Long Range Science Plan 2013 is the need for nimble methods for reconnaissance recovery of small rock cores near ice margins. In response to this, IDPO-IDDO is initiating work on a new Shallow Basal Material Recovery Drill designed primarily to retrieve bedrock samples beneath ice that is up to 200 to 300m thick, and will be easily transportable. The first use of this drill is planned for Antarctic field season 2015-2016 for recovery of rock pieces under several hundred meters of ice.
Rapid Access Hot Water Drill
During Program Year 2014, IDPO-IDDO is initiating the design of a new Rapid Access Hot Water Drill that has a modular capability to accommodate creation of access holes of different diameters from 500 m up to 2,500 m in depth. This drill will support requests from the community for investigating basal conditions and geothermal flux, sub-ice shelf mass balance, grounding zone processes, and sub-ice microbial ecosystems and biogeochemistry.
Equipment Development (2013 Summer)
Intermediate Depth Drill
IDDO continued work on the procurement of the Intermediate Depth Drill (IDD) parts and components and started system fabrication, assembly, and components testing. The final assembly of the entire system is planned to be completed by September 30, 2013.
IDPO-IDDO continued to work with the NSF Arctic Logistic contractor (CH2M Hill Polar Services) on the field logistics required for the 2014 IDD field test in Greenland. The Estisol-140 drilling fluid and borehole casing needed for the test were also purchased and are currently on vessel for delivery in Thule, Greenland for subsequent transportation to the field test site (the proposed Isi Station; ~3 miles due north of Summit Station) via the Greenland Traverse in April 2014.
Deep Logging Winch
The Deep Logging Winch system is currently in production and is scheduled for delivery to IDDO by August 15th by Markey Machinery Co. IDDO designed and placed a purchase order for the winch sled and, working with the winch manufacturer, modified the winch control system.
Blue Ice Drill-Deep
After finishing the design and fabrication of a new anti-torque and modifications of the cutter heads for the Blue Ice Drill-Deep (BID-Deep), IDDO successfully completed testing of firn coring capabilities in Greenland in May of 2013. IDDO plans to finish the entire BID-Deep design by September 30, 2013.
DISC Drill/Replicate Coring System
By June of 2013, IDDO completed the preparation of many DISC/Replicate Coring System components for storage. Small repairs, upgrades, and the necessary component maintenance have been completed. IDDO also developed a comprehensive list of all mechanical and electrical subsystem modifications and repairs needed for the drill's future re-deployment.
Scientific Drilling (2013 Arctic field season)
Denali (PI Osterberg)
IDDO provided driller Mike Waszkiewicz and a Eclipse Drill for PI Erich Osterberg's coring project in Denali National Park. Two holes were completed down to a depth of 208 meters each, resulting in excellent core quality. A new solar and wind system capable of powering the Badger-Eclipse Drill proved successful on its maiden field project. Such clean drilling efforts were praised by National Park Service staff and will continue to be utilized in the future.
Greenland Aerosol and Greenhouse Gases Core (PI McConnell)
Despite being forestalled by weather in previous attempts to drill ice cores on Tunu Glacier in Greenland several years ago, IDDO driller Bella Bergeron and the science field team were able to recover successfully over 350 meters of ice core during the month of May. Using an IDDO 4-Inch Drill, one hole was completed down to 213 meters while a second hole was completed down to 141 meters.
Greenland Cosmogenic C-14 Cores (PI Petrenko)
A team of three IDDO drillers, Lou Albershardt, Mike Jayred, and Tanner Kuhl, accompanied by a field science team was able to successfully utilize a Eclipse Drill to drill two holes for firn air pumping studies outside of Summit Station, Greenland. One hole was completed to 90 meters and another completed to 102 meters. In addition, the IDDO-designed Blue Ice Drill was put to the test to determine its ability to collect firn cores. The Blue Ice Drill is expected to undergo several modifications over the next year to enable additional firn coring in Greenland as well as to extend its depth capabilities in both firn and ice.
Greenland Perennial Firn Aquifer (PI Forster)
As a follow up to a previous project conducted by PI Rick Forster in SE Greenland, IDDO provided driller Jay Kyne and the IDDO Thermal Drill to drill through the firn aquifer layer. Two holes were completed down to 60 meter and 25 meters, respectively, each allowing the deployment of a thermistor string through the aquifer.
McCall Glacier Cores (PI Nolan)
PI Matt Nolan completed his third season of a three-year ice coring project on McCall Glacier in Alaska. Throughout the project, Nolan utilized both a 3-Inch and 4-Inch PICO Hand Auger to retrieve shallow core samples.
Summit Shallow Core Array (PI Noone)
PI David Noone's field team deployed late in the third quarter to continue their collection of shallow ice cores near Summit Station. To support this work, IDDO again provided a PICO hand auger and a new IDDO hand auger as well as a Sidewinder power drive system. This year marks the third year of IDDO's support of the four-year project.
Equipment Development (2013 Spring)
Intermediate Depth Drill
IDDO continued work on the design and fabrication of the Intermediate Depth Drill (IDD). On March 20, IDDO held a web-based Final IDD System Engineering Design Review with the South Pole Ice Core PIs, along with several members from the IDPO Science Advisory Board, the IDDO Technical Advisory Board, and IDPO personnel. The final system design has been approved, and IDDO is actively procuring IDD system components and support equipment. The presentation from the Final IDD System Engineering Design Review is available for download at:
https://icedrill.org/library/intermediate-depth-drill-final-system-engineering-design-review-20-march-2013
Deep Logging Winch
IDDO finished specifications of the 4000-meter Deep Logging Winch and placed an order with Markey Machinery Company, Seattle, WA. On March 19, IDDO approved the certified drawings of the entire system developed by the manufacturer, and the winch is in the process of being produced.
Blue Ice Drill-Deep
IDDO finished the final design and procured all components for the modified Blue Ice Drill-Deep. The system has been completed and shipped to Greenland for testing by PI Vas Petrenko during the 2013 Arctic field season. Previously, the Blue Ice Drill had only been used to collected large diameter cores (9.5 inches) to depths of approximately 25 meters in blue ice. The modifications to the Blue Ice Drill are expected to allow it to now also collect large diameter cores (9.5 inches) in firn and to depths in excess of 100 meters.
Drilling Completed at Taylor Glacier, Antarctica for Study of Ancient Atmospheres
Using the Blue Ice Drill developed by IDDO, an IDDO contract driller successfully completed drilling for samples dedicated to the study of ancient atmospheric composition. Over 800 meters of high quality, large (9.5-inch diameter) ice core was recovered, bringing the drilling to a successful completion on schedule. The science experiment, led by PI Jeff Severinghaus, provides unique and important evidence of past atmospheric composition.
New Drilling Technology Enables Study of Ancient Atmospheres
The new Blue Ice Drill, designed and built for the University of California - San Diego with ARRA funding from NSF-OPP, was deployed to the field for the first time in Taylor Valley, Antarctica with resounding success. The drill design proved very effective for collecting large volumes of ice in a short period of time. Over 600 meters of high quality, large (9.5-inch diameter) ice core was recovered and at a faster rate than anticipated. The large quantity of high quality core, which is needed to effectively measure rate gases, was melted and analyzed on site. The science experiment, led by PI Jeff Severinghaus, provides unique and important evidence of past atmospheric composition. The Blue Ice Drill will be used again in 2011-2012 for the second field season of the project.
Overview of Activities (2011 Spring)
The second quarter FY2011 yielded success on many fronts for IDPO and IDDO. Of particular note is the reaching of the drilling goal of 3,331 meters using the DISC Drill at WAIS Divide, Antarctica, becoming the deepest U.S. ice core ever drilled. The newly-developed Blue Ice Drill achieved and surpassed its design requirements at Taylor Valley, Antarctica for drilling large volumes of ice in a short amount of time; over 600 meters of high quality, large (9.5-inch diameter) ice core was recovered at a rate faster than anticipated. IDPO worked with the community and with IDDO to discuss implications of the science requirements for the future intermediate depth drill design, cost estimates, and potential collaborations. The most critical issues currently facing IDDO are the repair and updating of the DISC Drill after the 2010-2011 WAIS Divide field season and the development of the DISC Drill Replicate Coring System, which is scheduled for testing at WAIS Divide during the 2011-2012 Antarctic field season.