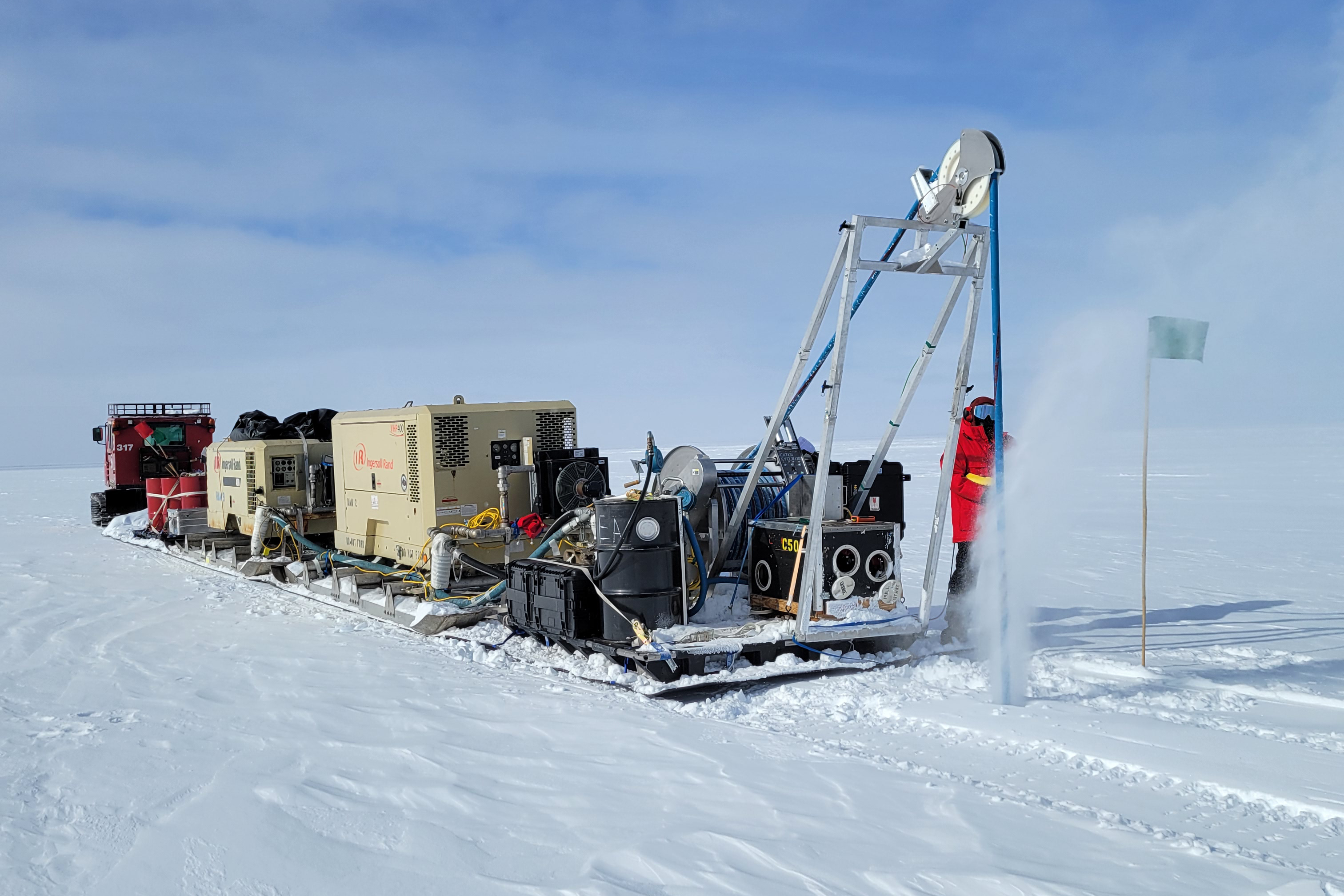
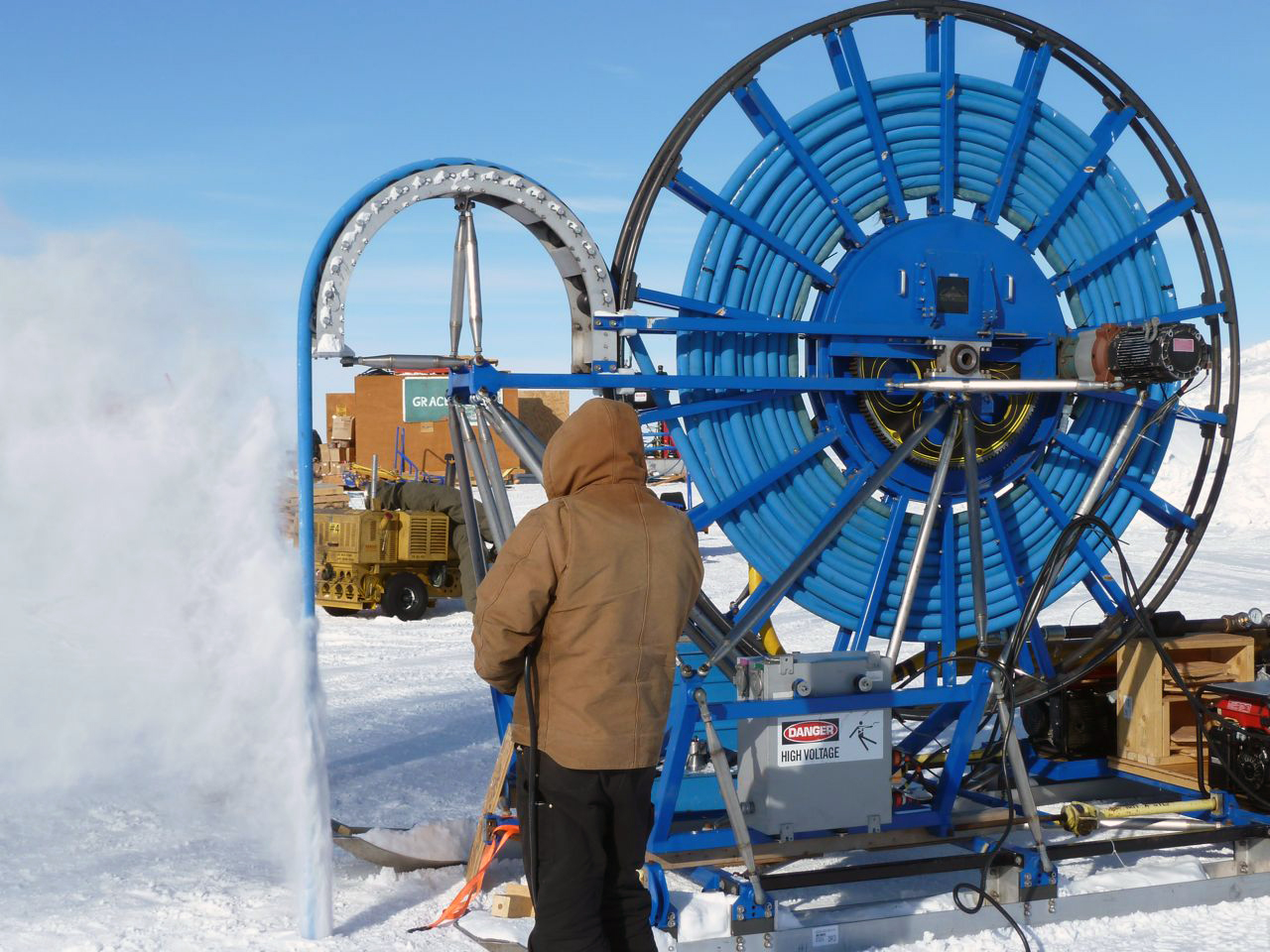
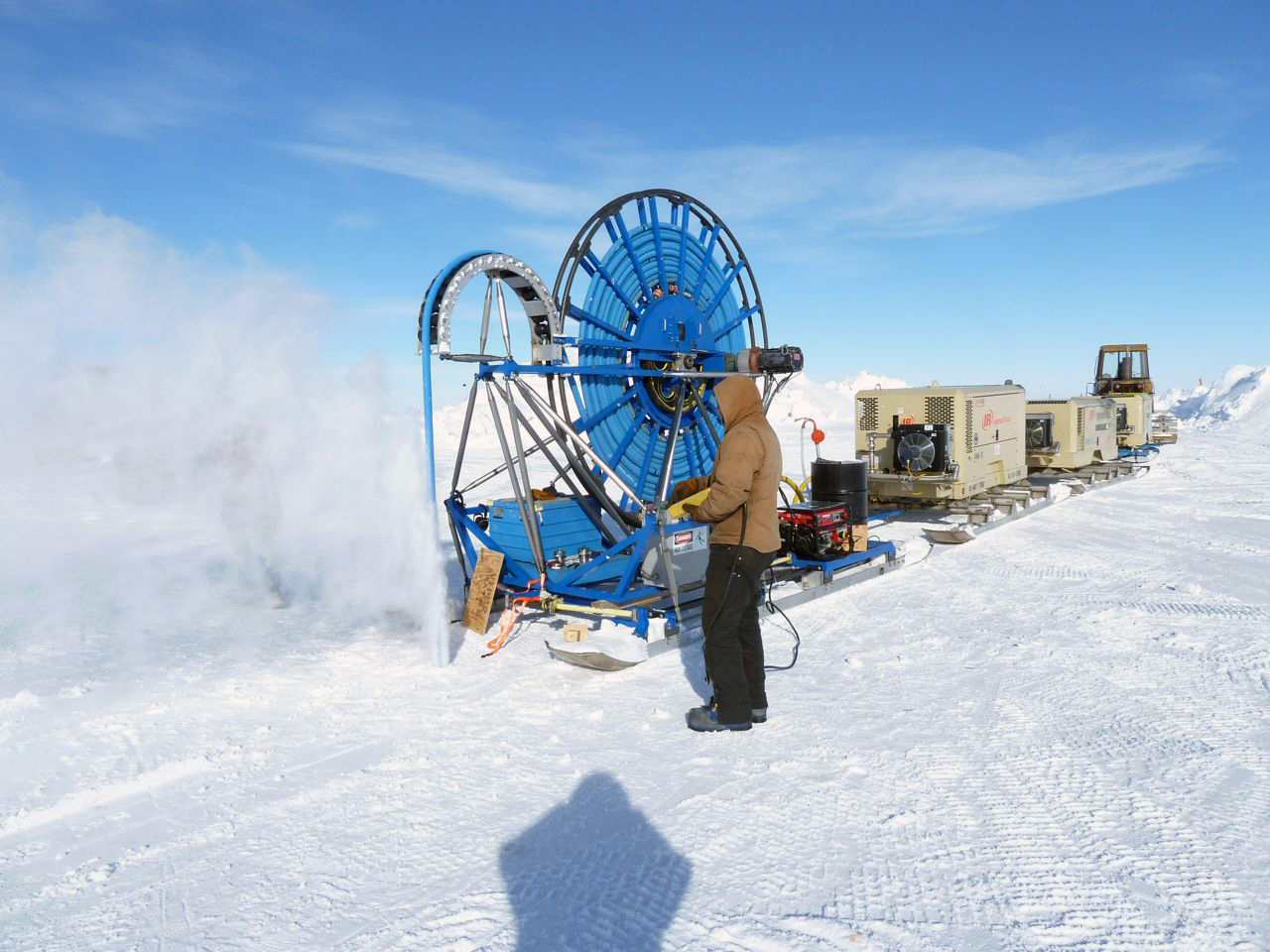
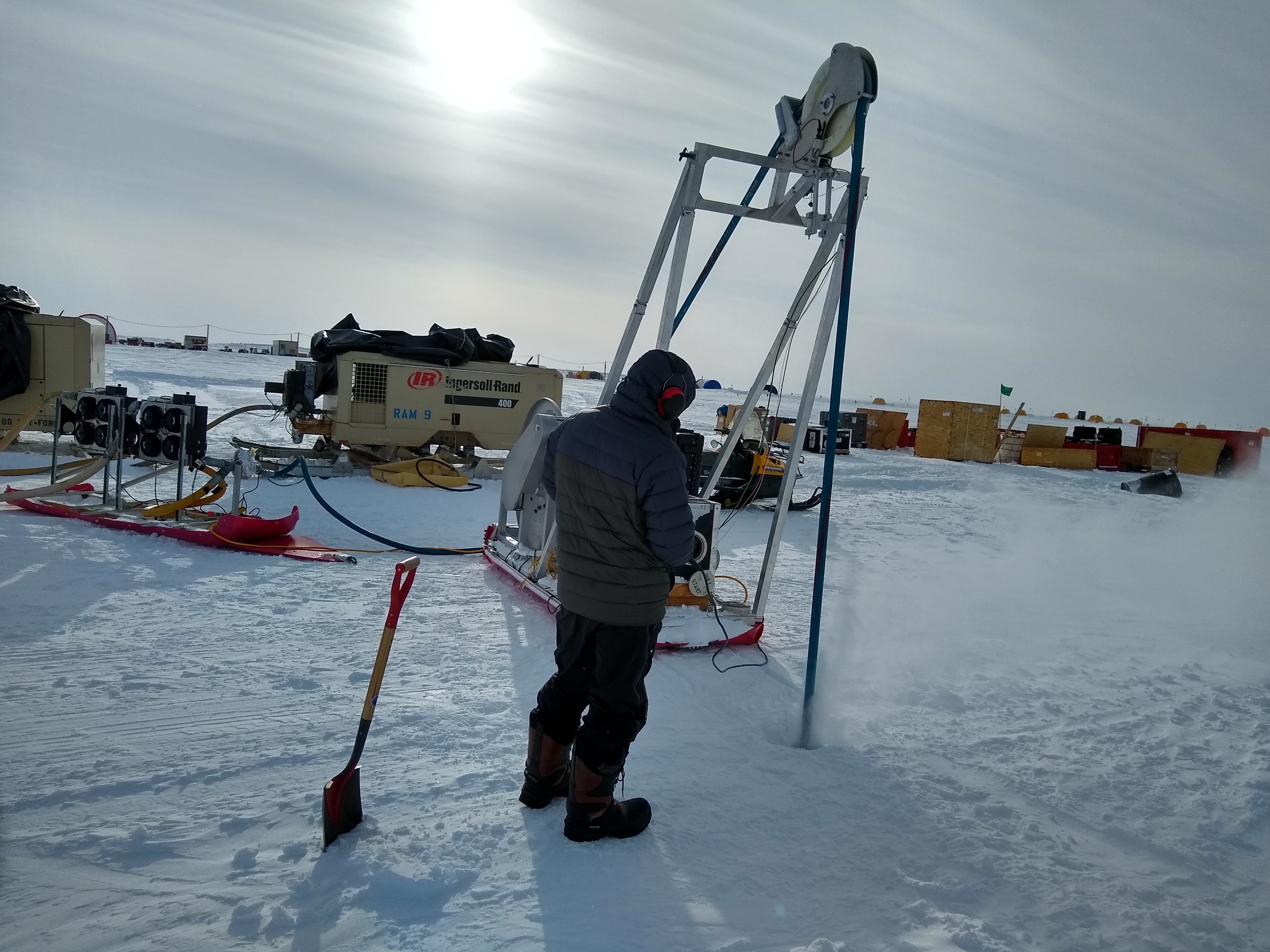
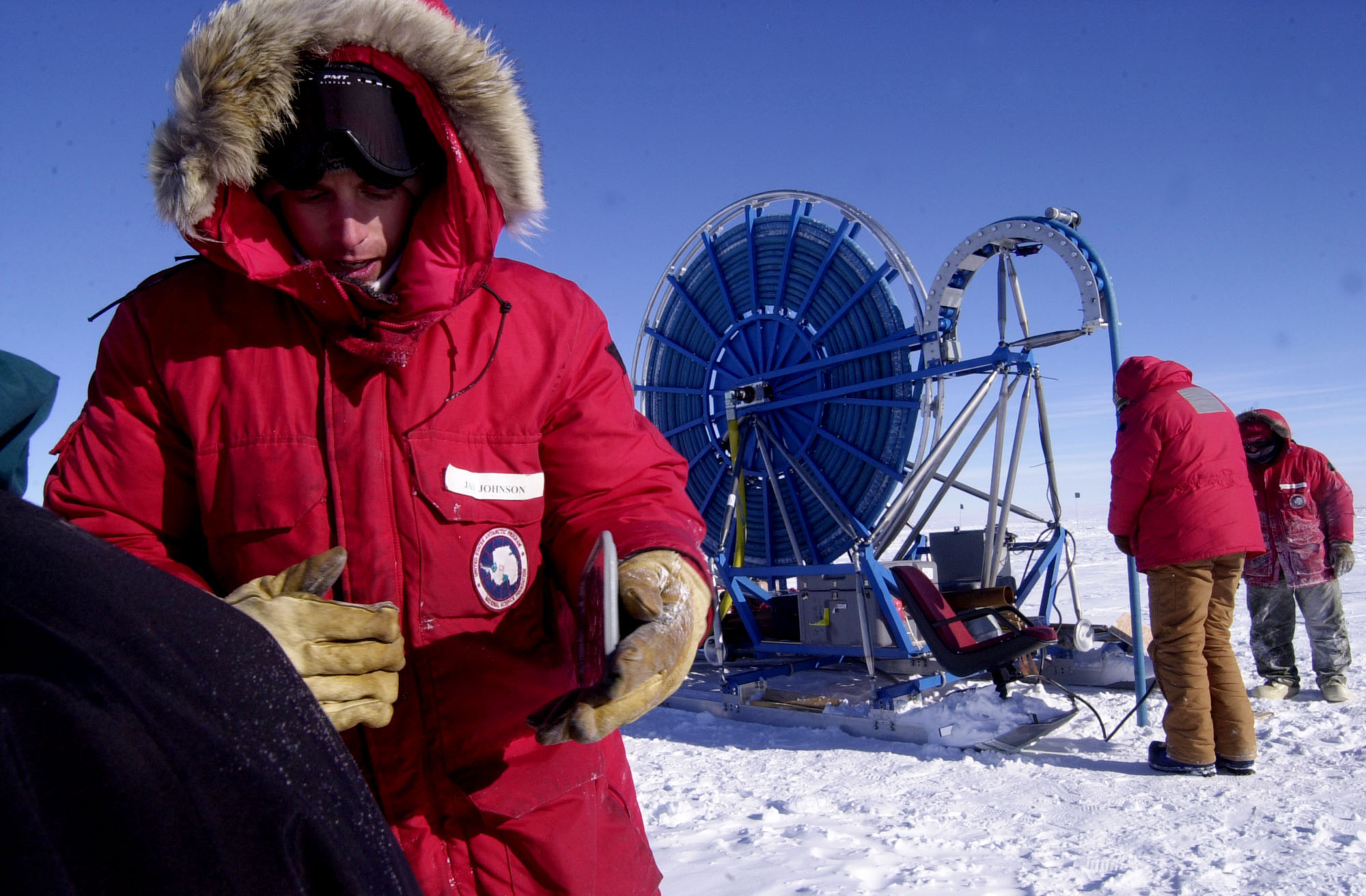
The Rapid Air Movement (RAM) Drill was developed for creating shot holes for seismic geophysical exploration. It is a system in which high-velocity air drives rotating cutters and blows the ice chips from the hole. The cutting drill motor hangs on a hose that carries the air from the surface and is reeled out as the hole deepens. The original RAM Drill was used three times in West Antarctica, where it routinely achieved depths of 90 meters. The Askaryan Radio Array (ARA) project used the drill in 2010-2011 to test methods of producing holes for radio antennae at South Pole but could not get deeper than 63 meters at that location.
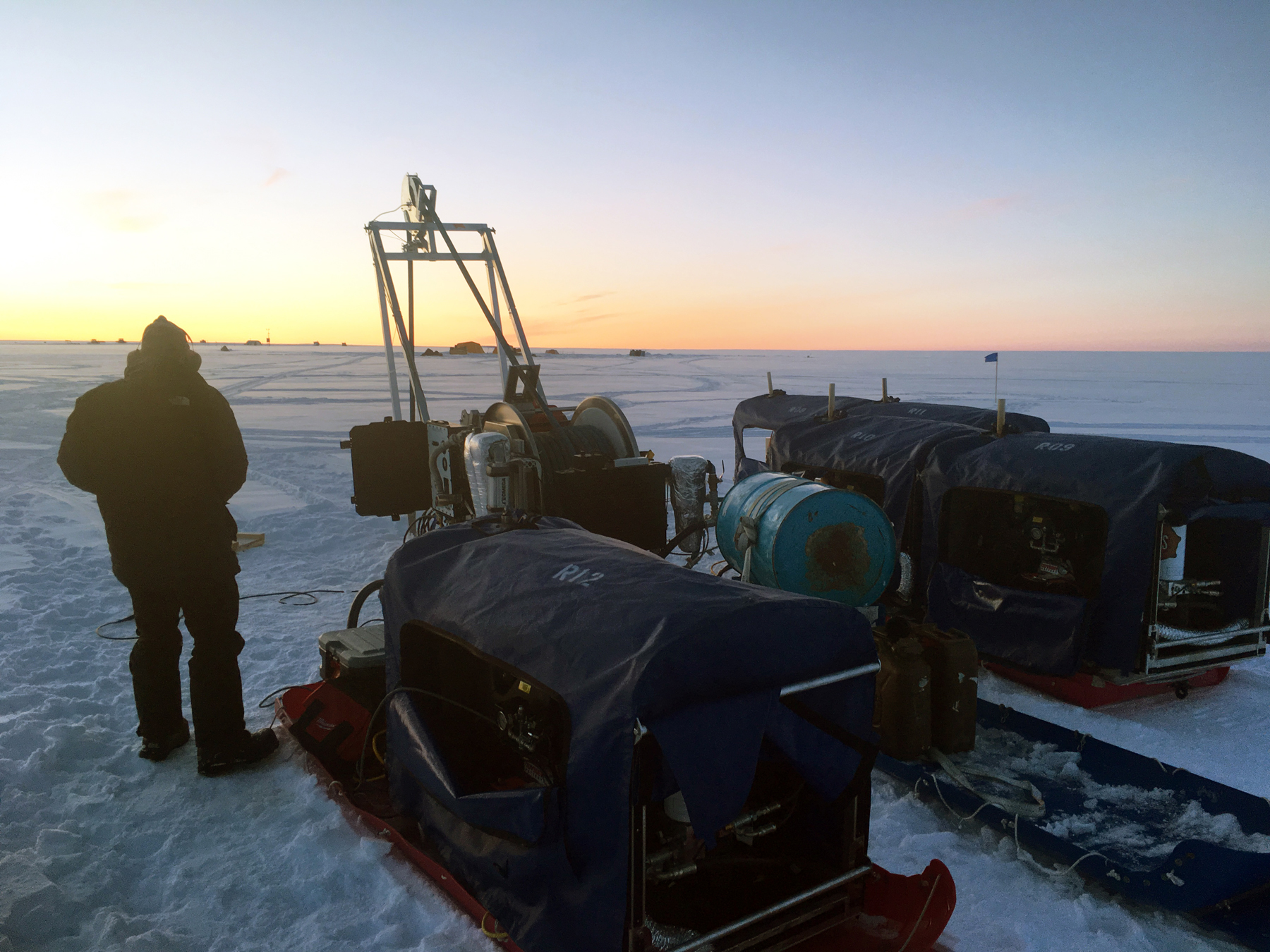
In 2017, substantial modifications and upgrades were made to reduce the system’s logistical requirements. IDP designed and built the modified RAM 2 system. The modifications serve to dramatically reduce the system weight and should allow for easier assembly and operations in remote areas. A field test of the modified system was conducted near Raven Camp in Greenland in July 2018. Repairs and additional modifications were made prior to the drill’s deployment to Antarctica in September 2018. The system was tested by two IDP personnel at WAIS Divide during the 2019-2020 field season where the drill routinely achieved between 50-55 meters. Smaller RAM 2 compressors will eventually be optimized to provide the necessary airflow for future projects.
During an abbreviated 2022-2023 Antarctic season, the RAM 2 Drill was used to drill 27 holes and operational data for the RAM 2 Drill system was collected. The system was used again during the 2023-2024 season to drill 13 holes to a max depth of 45 meters near WAIS Divide Camp. The system was to be used on Thwaites Glacier, but the PistenBully 100 provided to tow the drill was inadequate, causing the traverse to continuously become stuck in the warmer snow near Thwaites. The Small Hot Water Drill was used in place of the RAM Drill.
Equipment Details
| Name | Rapid Air Movement Drill |
|---|---|
| Type |
Type
Non-coring
|
| Number in Inventory |
Number in Inventory
1
|
| Max. Practical Depth |
Max. Practical Depth
95 m (the depth being limited by the length of the hose)
|
| Hole Diameter |
Hole Diameter
100 mm
|
| IDP Driller Required? |
IDP Driller Required?
Yes, 2 drillers
|
| Drill Fluid Required? |
Drill Fluid Required?
No
|
| Shipping Weight |
Shipping Weight
18,853 lbs |
| Shipping Volume (Cube) |
Shipping Cube
1649 cube |
| Restrictions |
Restrictions
Optimization of the compressors (small or large) and the hose and sonde are required to meet the revised science requirements for RAM 2. Even with the large compressors, however, the drill system is not reaching the 90 m depth range of the original RAM Drill. |
Documents
| Citation | Year |
|---|---|
| Chris J Gibson, Grant Boeckmann, Zachary Meulemans, Tanner W Kuhl, Jim Koehler, Jay A Johnson, Kristina R Slawny (2021) RAM-2 Drill system development: an upgrade of the Rapid Air Movement Drill. Annals of Glaciology, 62, (84), 99-108. doi: 10.1017/aog.2020.72. https://doi.org/10.1017/aog.2020.72 | 2021 |
| NSF Ice Drilling Program (2020) Rapid Air Movement Drill 2 Operations and Maintenance Manual Configuration-1. 1-11. | 2020 |
| Sridhar Anandakrishnan, Paul Winberry, IDPO (2017) Science Requirements: RAM Drill. | 2017 |
| Chris J Gibson, Jay A Johnson, Grant Boeckmann (2017) Rapid Air Movement (RAM) Drill Upgrade Concept Overview. 1-18. | 2017 |
| IDDO (2017) Rapid Air Movement (RAM) Drill Upgrade Conceptual Design Review. 1-26. | 2017 |
| Rusheng Wang, Liu An, Pinlu Cao, Baoyi Chen, Mikhail Sysoev, Dayou Fan, Pavel Talalay (2017) Rapid ice drilling with continual air transport of cuttings and cores: General concept. Polar Science, 14, 21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.polar.2017.09.004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polar.2017.09.004 | 2017 |
| Amber N Whelsky, Mary R Albert (2016) Firn permeability impacts on pressure loss associated with rapid air movement drilling. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 123, 149-154. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.11.018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.11.018 | 2016 |
Photos
Operating the RAM Drill at WAIS Divide, Antarctica, during the 2023/24 field season. Credit: Tanner Kuhl.
IDP driller Mike Jayred tests the RAM Drill during the 2010-2011 field season for the Askaryan Radio Array project at South Pole. Photo: Michael DuVernois